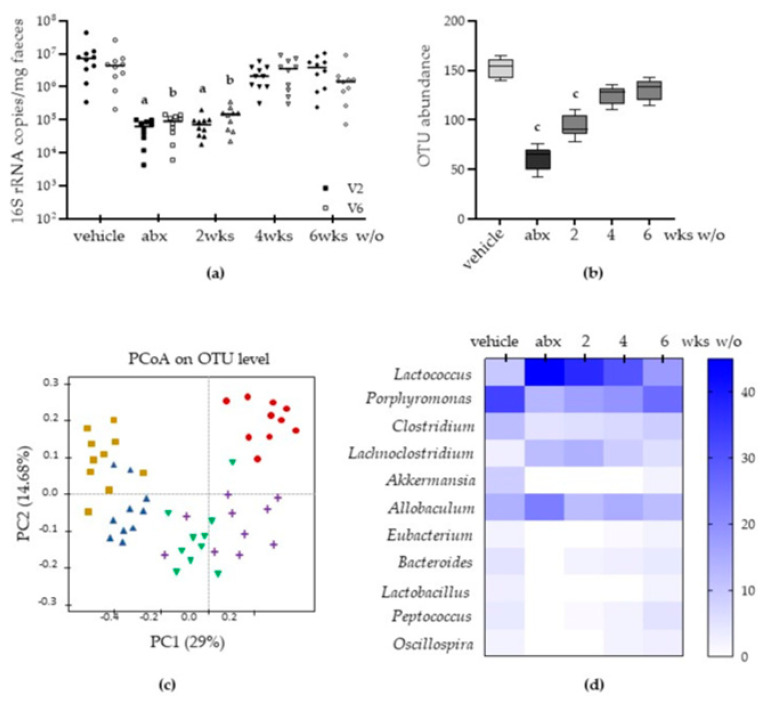
Figure 1.
Mice were treated with vehicle or antibiotic mixture (abx) and sacrificed 2 weeks (wks) later; otherwise, mice were treated with abx and sacrificed 2, 4, or 6 weeks (wks) post antibiotic wash-out (w/o). The total bacterial load was estimated from the DNA isolated from the cecal content with qPCR using primers for the V2 and V6 regions of bacterial 16S genes. Dark circle: V2, vehicle; grey circle: V6 vehicle; dark square: V2 abx; grey square: V6 abx; dark up-triangle: V2 2 wks wash-out; grey up-triangle: V6 2 wks wash-out; dark down-triangle: V2 4wks wash-out; grey down-triangle: V6 4 wks wash-out; dark rhombus: V2 6 wks wash-out; grey rhombus: V6 6 wks wash-out (a). DNA was sequenced using Illumina MiSeq chemistry; operational taxonomic unit (OTU) relative abundance is reported. Light grey: vehicle; dark grey: abx treatement; intermediate grey: wash-out. (b). Taxonomical differences among samples were determined using principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) (c). The average relative abundance percentage for the 11 most abundant genera is displayed (d). Data are reported as mean ± SD; number of mice for each experimental group = 10 mice per group; a denotes p < 0.02 vs. V2 copy number in vehicle-treated mice; b denotes p < 0.02 vs. V6 copy number in vehicle-treated mice; c denotes p < 0.05 vs. vehicle-treated mice.