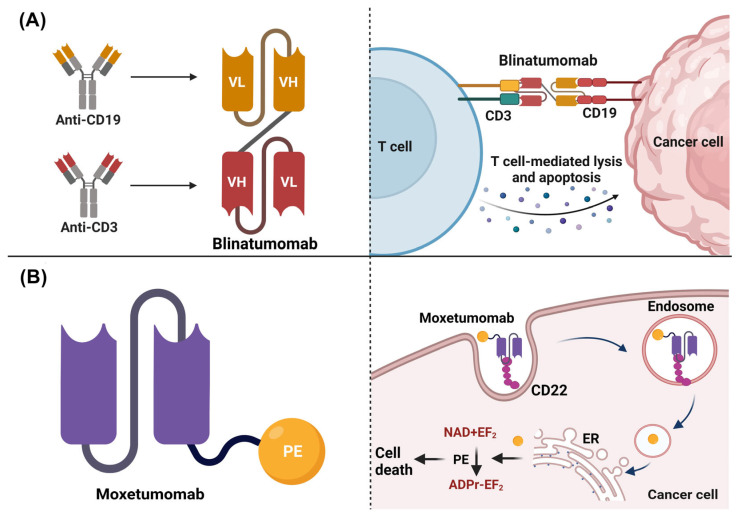
Figure 4.
Structure and mechanisms of action of scFv approved by the FDA. (A) Blinatumomab structure and mechanism of action. It is composed of variable fragments of bivalent bispecific antibodies linked together. Blinatumomab stimulates a synapse between the CD3+ T cell and the CD19+ tumoral target cells, promoting the upregulation of adhesion molecules, production of cytolytic proteins, and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines that conveyed to cellular lysis and apoptosis of the CD19+ cells. (B) Moxetumomab pasudotox structure and mechanism of action. It involves an anti-CD22 scFv linked to Pseudomonas exotoxin A PE38 by a peptide bond to VH. Moxetumomab binds to CD22 overexpressed in malignant B cells; later, the complex Moxetumomab-CD22 is internalized by endocytosis. Finally, PE38 catalyzes the ADP-ribosylation of the diphthamide residue in EF-2, which promotes a reduction in the levels of the antiapoptotic protein Mcl-1 and increases the apoptotic rate. Image created in BioRender (www.biorender.com, accessed on 20 January 2023).