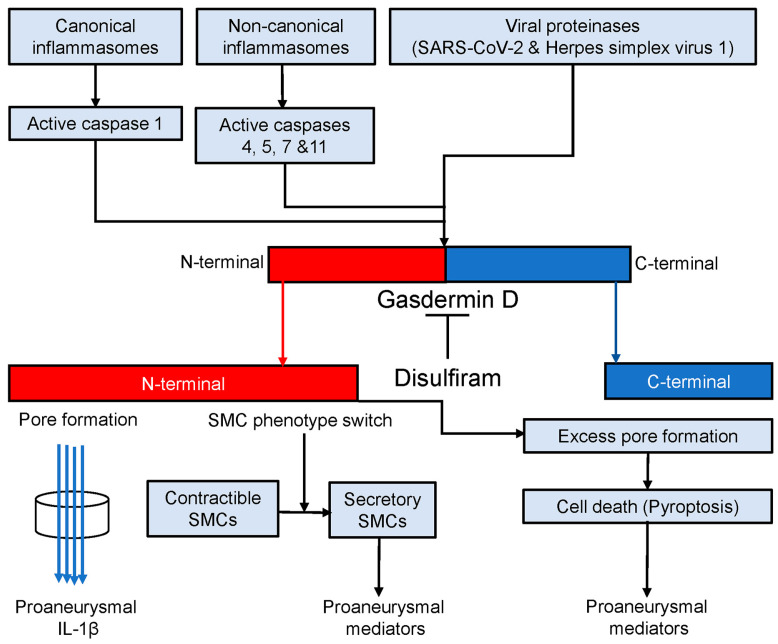
Figure 7.
Gasdermin D in AAA pathogenesis. Canonical and noncanonical inflammasome activation and viral proteinases convert procaspases 1, 4, 5, 7, and 11 to corresponding active forms which activates gasdermin D by cleaving it to N- and C-terminals. The C-terminal forms the membrane pores through which proaneurysmal interleukin 1β is secreted. Cell death (pyroptosis) due to excess pore formation also releases various types of intracellular proaneurysmal mediators including cytokines. Alternatively, gasdermin D activation switches smooth muscle cells (SMCs) from contractible towards secretory phenotype leading to proaneurysmal mediator release. Disulfiram blocks active caspase-mediated gasdermin D cleavage and thus suppresses experimental AAAs probably in pore-dependent and -independent manners.