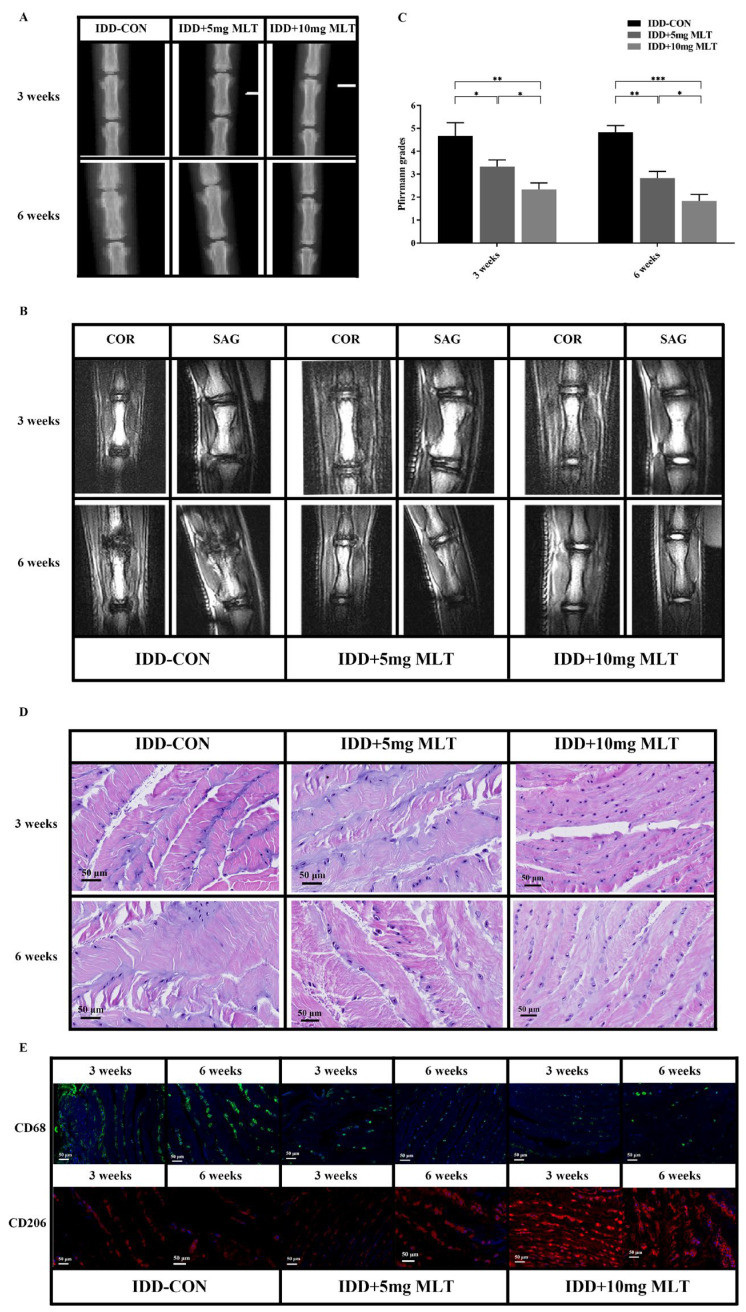
Figure 6.
Inhibition of M1-type Mφ polarization by MLT ameliorates IDD in vivo. Rat models of IDD were established by caudal IVD puncture surgery and with the treatment of MLT for 1 week, then followed by different analysis at 3 weeks and 6 weeks after surgery. (A) The representative X-ray radiographs showed the different heights of IVDs in different groups at 3 weeks and 6 weeks after surgery. The height of IVDs in the IDD control group was lower than that in the MLT-treated groups both at 3 and 6 weeks. (B) The representative coronal (COR) and sagittal (SAG) MRI of every group at 3 weeks and 6 weeks after surgery. The MLT-treated groups had higher IVD height and T2-weighted signal intensity when compared with the IDD control group at both 3 and 6 weeks. (C) The Pfirrmann grade scores of the IVDs in each group assessed by the results of T2-weighted MRI to quantify the degeneration degree of IVDs (n = 3). The Pfirrmann grades were significantly lower in the MLT-treated groups relative to those in the IDD control group at both 3 and 6 weeks. (D) H&E staining of IVD tissues at 3 weeks and 6 weeks after surgery showed the degrees of degeneration in IVDs in different groups. The NP cells showed reduced size and number and were surrounded by disorganized AF, and the cells of IVDs were clustered and the striped matrices were distributed among the cell clusters in the IDD-control group, while the morphological changes of NP cells and the degrees of the firosis and structural disorder of IVDs were markedly ameliorated in the MLT-treated groups. (E) The condition of Mφ polarization in IVD tissues at 3 weeks and 6 weeks after surgery were measured by immunofluorescence. M1-type Mφs (CD68+, green) decreased, while M2-type Mφs (CD206+, red) increased in the MLT-treated groups when compared with the IDD-control group, both at 3 and 6 weeks. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The two groups among the three groups are compared by using an independent t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001.