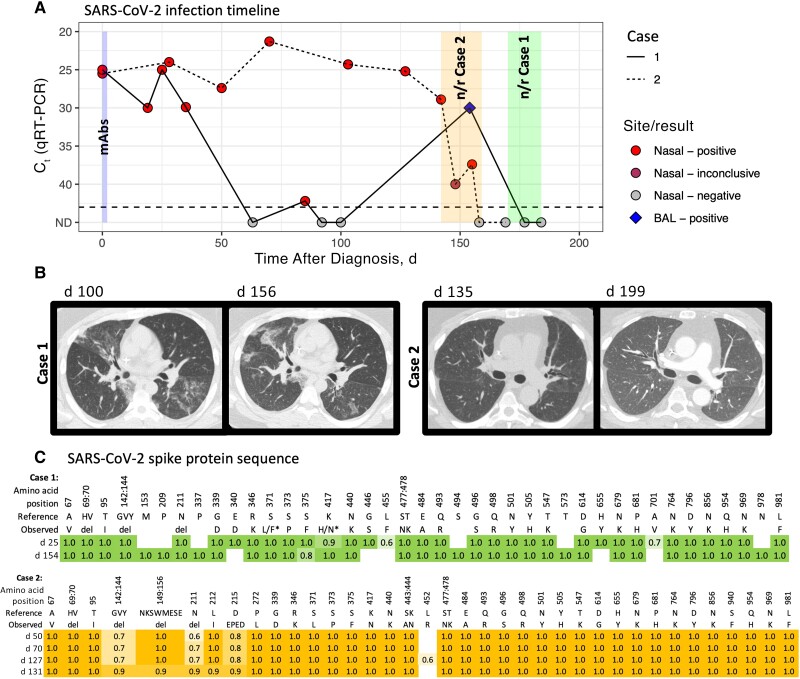
Figure 1.
A, Timeline of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) detection with quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) from respiratory site samples (nasal swab and bronchoalveolar lavage [BAL]) in cases 1 (solid line) and 2 (dotted line). Tests where no virus was detected are indicated in gray (not detected [ND]). qRT-PCR assays were performed in a clinical laboratory, which uses multiple testing platforms, including Cepheid, Hologic, Cobas, Abbott, and Diasorin. Cycle threshold (Ct) values are presented, with lower values indicating higher viral loads, and higher values, lower viral loads. Nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (n/r) treatment was started on day 170 in case 1 (continued for 15 days) and on day 142 in case 2 (continued for 18 days). Nasal swab samples are depicted by a circle, and BAL samples by a diamond. Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) were administered on day 1 or 2 of symptoms, sotrovimab in case 1 and bebtelovimab in case 2. B, Chest computed tomographic scans in cases 1 (left) and 2 (right) during illness and treatment. C, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein amino acid sequences over the course of illness by day after symptom onset. Consensus sequence (>50% allelic frequency) changes from reference sequence NC_045512.2 (Wuhan Hu 1) are shown. Omicron variant BA.1.1 was detected in both cases. The asterisks in the sequence for case 1 indicate 2 positions where amino acid consensus differed between the 2 samples (L/F and H/N, where the day 25 sequence is indicated first). Abbreviation: del, deletion.