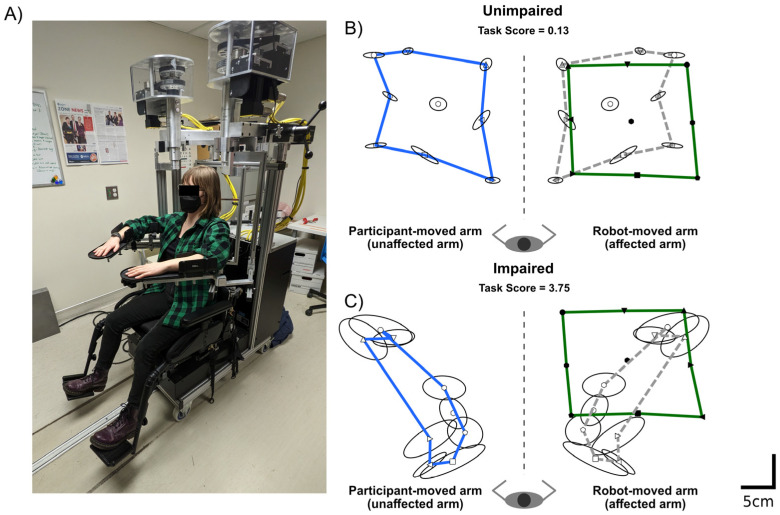
Figure 1.
Robotic Assessment of Proprioception—(A) Kinarm Exoskeleton Lab (Kingston, ON, Canada) used to perform the robotic assessment of proprioception (Arm Position Matching task). (B) Exemplar Arm Position Matching task performance of an unimpaired stroke participant. The robot moved the affected right arm. Closed symbols indicate the mean nine target positions where the robot moved the participant’s hand. For illustrative purposes, the green line connects the mean hand position of the eight outer targets. The participant matched with their unaffected left arm. Open symbols indicate the mean, matched hand position of the unaffected arm. Again, for illustrative purposes, the blue line connects the eight outer targets. Ellipsoids represent the variability (one standard deviation) in matched position around each target. For illustrative purposes, the participant’s matched positions have been reflected across the midline onto the robot moved arm. The dashed grey line connects the reflected outer 8 targets. (C) Same format as B, except an exemplar from a stroke participant with an impairment on the Arm Position Matching task is provided.