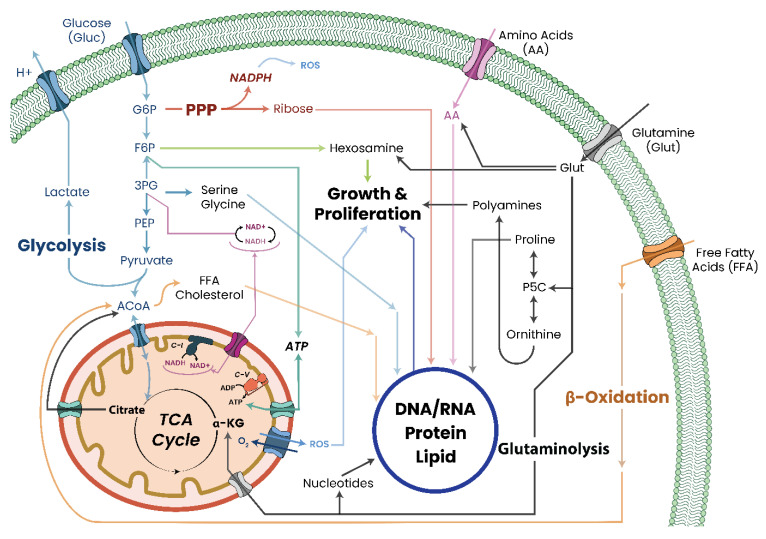
Figure 6.
Schematic outlining the relationships between cellular metabolic pathways and the mitochondria. Although separate, each metabolic pathway within the cell feeds back into the mitochondria by producing metabolites required for ATP production. Deficiency/damage/inhibition to any of metabolic pathway can result in metabolic deficiency, potentially triggering an RTG response. Legend: G6P—glucose-6-phosphate; F6P—fructose-6-phosphate; 3PG—glycerate-3-phosphate; PEP—phosphoenolpyruvate; ACoA—acetyl coenzyme A; α-KG—α-ketoglutarate; PPP—pentose phosphate pathway; P5C—1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate; TCA—tricarboxylic acid; ROS—reactive oxygen species and conditions [240]. Mitochondrial dysfunction can therefore be a major contributing factor to a varied range of pathologies with potentially serious debilitating and/or life-threatening consequences.