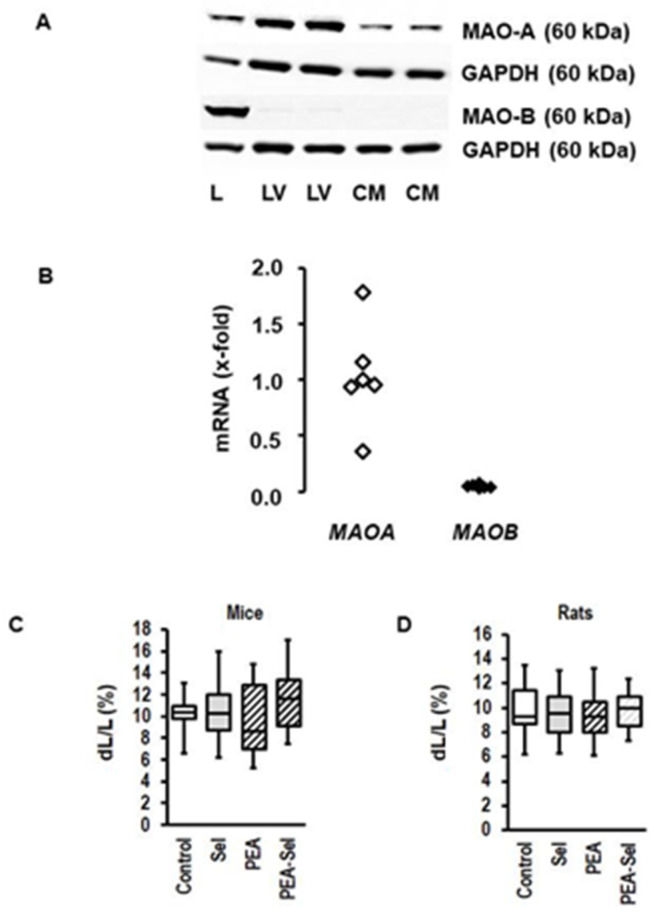
Figure 2.
Expression of MAO isoforms in rat heart and myocytes and effect of MAO-B activation on mouse and rat myocytes. (A) Western blot indicating the expression of MAO-A and MAO-B in the liver (L), left ventricle (LV), and cardiomyocytes (CM) from rat hearts. GAPDH was used as loading control. (B) mRNA expression in rat hearts of the genes (MAOA; MAOB) encoding for MAO-A and MAO-B. The data are normalized to beta-2-microglobulin (b2m) as a housekeeping gene. The mean of MAOA expression is set as 1. (C) Load-free cell shortening is expressed as % shortening amplitude (dL) normalized to the diastolic cell length (L). Data are full ranges (whiskers) with median and 25 and 75% quartiles (boxes). Cells (isolated ventricular myocytes from mice) were incubated with selegiline (Sel; 1 µM; n = 26), β-phenylethylamine (PEA, 250 µM; n = 18), or combinations thereof (n = 27) for 24 h. Untreated controls (n = 18) were used to control the quality of the preparation. Cells were stimulated at 2 Hz and cell shortening was monitored by a line camera. (D) Similar experiment to C, but with rat myocytes (ARVM; n = 36 each).