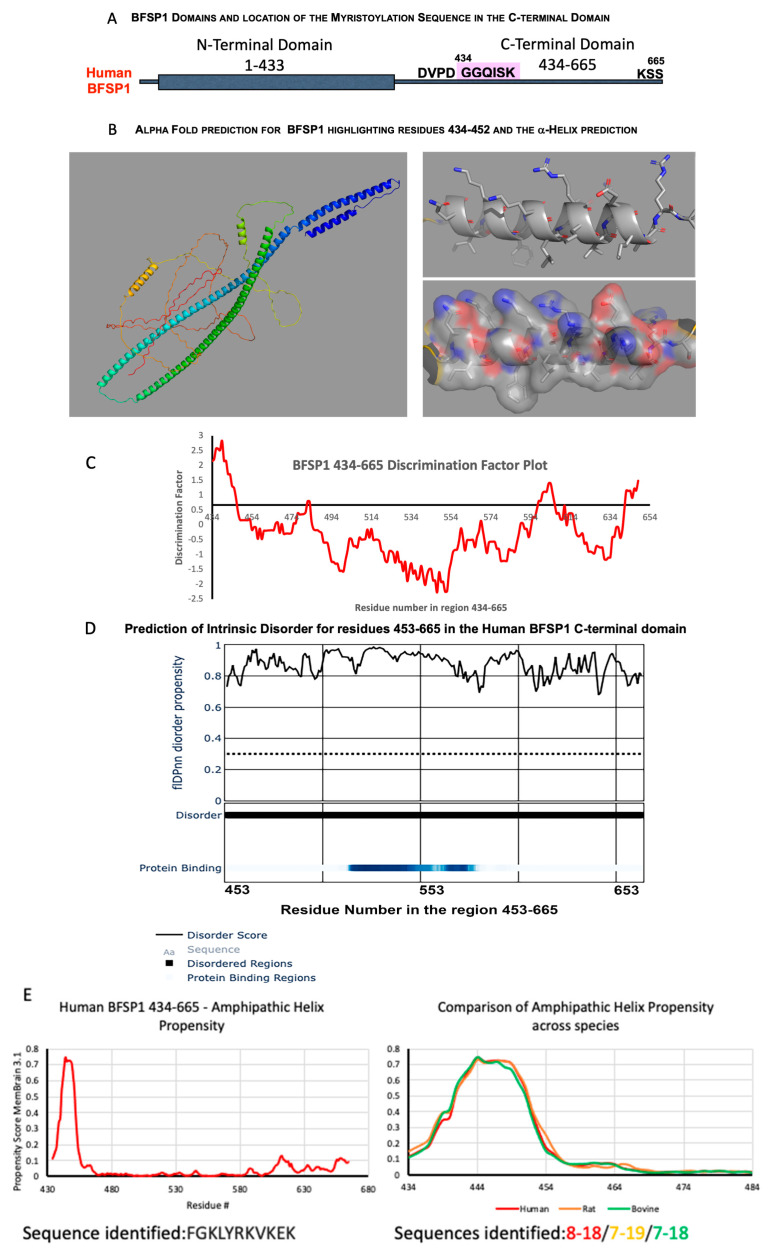
Figure 1.
Bioinformatic analyses of BFSP1 and its C-terminal sequences 434–665. Human BFSP1 is a 665-residue protein, with a large α-helical rod domain (grey rectangle) and a C-terminal domain containing a cryptic myristoylation site (GGQISK) that is released by caspase cleavage at site 433 (A). AlphaFold2 predicted with high confidence an α-helix for residues 434–452, whilst the remaining C-terminal sequences had low/very low secondary structure prediction (B). HELIQUEST was used to calculate the discrimination factor (DF) over the region 434–665, with the X-axis intersect set to a DF of 0.68 as the threshold for identifying LBDs. The strongest score was received for the sequence 434–453 (C), but others were identified starting at residues 597 and 641 in the absence of predicted α-helix. The C-terminal BFSP1 sequences (454–665) were predicted to have a considerable intrinsic disorder as predicted using the algorithm fIDPnn (D). A minimum threshold score of 0.3 is indicated (---), but most of the BFSP1 453–665 sequences scored ≥ 0.8, indicative of significant disorder potential (D). A region potentially involved in protein-protein interactions was identified between 520 and 550 (dark blue bar; D). The 434–665 sequences were assessed for their propensity to form amphipathic helices, and one region was identified within the BFSP1 region 434–455 (E). The same region was identified in rat and bovine sequences (E), in line with the observation that the caspase recognition site and the myristoylation sequences are highly conserved across species [18].