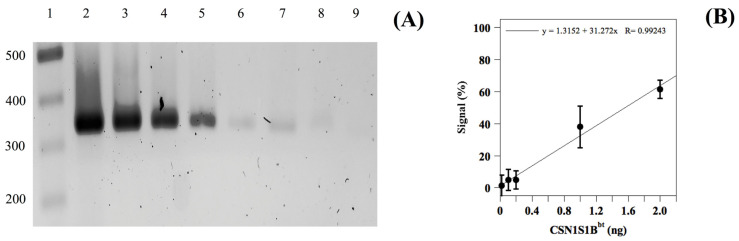
Figure 2.
Evaluation of the detection limit of heterozygous DNA (CSN1S1B/CSN1S1Bbt) from buffalo milk. Panel (A). AS-PCR products of buffalo milk of a single foreign animal containing heterozygous DNA (CSN1S1B/CSN1S1Bbt) progressively diluted with the counterpart from the PDO area containing homozygous DNA (CSN1S1B/CSN1S1B); reaction products were loaded onto 2% agarose gel. Lane 1, 100 bp DNA ladder; lane 2, non-diluted buffalo milk from Romania; lanes 3 to 8, buffalo milk of a single foreign animal progressively diluted (1:10, 1:50, 1:100, 1:500, 1:1000, and 1:5000) with the counterpart from the PDO area, respectively; lane 9, negative control. Panel (B). Densitometric analysis of the gel bands 4–8 reported in panel A using ImageJ software. Data are reported as the mean percentage values ± SD with respect to the result from lane 2 (used as 100%). The experiment was performed in triplicate.