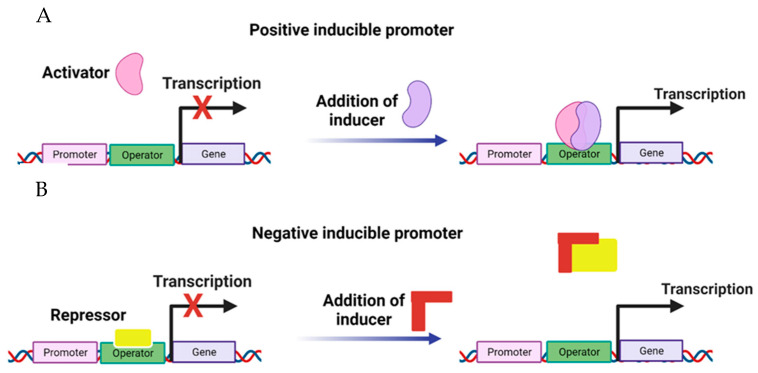
Figure 3.
Inducible promoters. In positive induction, (A) promoter inactivity occurs due to an activator (OFF) absence. When stimulation occurs, the activator binds to the DNA, causing transcription (ON). In negative induction, (B) a repressor binds to DNA, blocking the transcription process (OFF). Then, by the action of an inducer, the repressor is released, initiating transcription (ON).