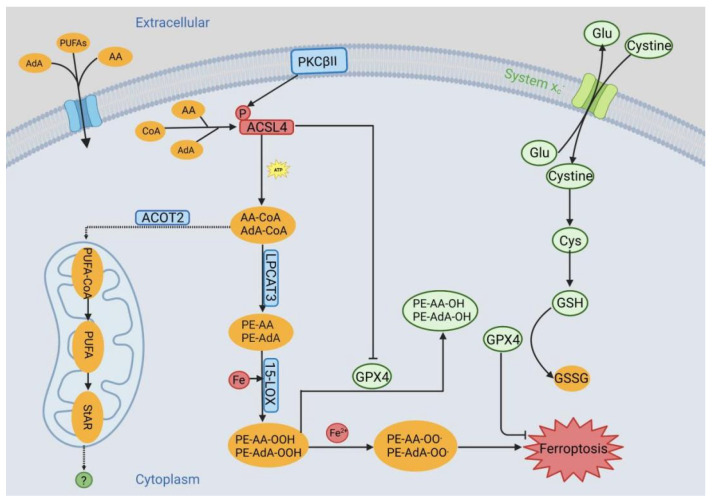
Figure 1.
During ferroptosis, PKCβII phosphorylates the Thr328 site of ACSL4, directly activating ACSL4 and facilitating the biosynthesis of PUFA lipids. PUFAs, primarily AA 20:4 and AdA 22:4, are activated by ACSL4 and then form PUFA-CoA by binding with coenzyme A (CoA) at the endoplasmic reticulum oxidation center, a process that consumes adenosine triphosphate (ATP). PUFA-CoA is esterified to PUFA-PE through the assistance of LPCAT3. Subsequently, it undergoes oxidation by 15-lipoxygenase (15-LOX), resulting in the production of lipid hydroperoxides that contribute to iron depletion. Additionally, Fe2+ can be released from the labile iron pool, leading to the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) such as HO· through the Fenton reaction. Consequently, lipid peroxides, including LOOH, can accumulate via a similar reaction mediated by Fe, resulting in a chain reaction that produces a significant number of lipid radicals. System XC− facilitates the exchange of cysteine and glutamate, enabling highly specific cysteine uptake. Once cysteine enters the cytoplasm, it undergoes reduction to cysteine, followed by catalysis by γ-glutamylcysteine synthase (γ-GCS) and glutathione synthase (GSS) to produce glutathione from cysteine. Two molecules of reduced glutathione (GSH) serve as electron donors, reducing PE-AA-OOH and PE-AdA-OOH to their respective alcohols, PE-AA-OH and PE-AdA-OH, and generating oxidized glutathione. Furthermore, ACSL4 directly inhibits GPX4, leading to ferroptosis. However, steroid-producing cells regulate the release of AA through the ACOT2 pathway. In this pathway, ACSL4 catalyzes the conversion of intracellular free AA to AA-coenzyme A and supplies it to ACOT2, which subsequently releases AA into the mitochondria. The released AA is progressively metabolized through the lipoxygenase pathway, inducing StAR, although its role in ferroptosis remains unclear. PUFAs, polyunsaturated fatty acids; AA, Arachidonic Acid; AdA, Adrenal Acid; PUFA-CoA, Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid-Coenzyme A; AA-CoA, Arachidonic Acid-Coenzyme A; AdA-CoA, Adrenal Acid-Coenzyme A; ATP, Adenosine Triphosphate; LPCAT3, Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3; PE-AA, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Arachidonic Acid; PE-AA, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Adrenal Acid; 15-LOX, 15-lipoxygenase; PE-AA-OOH, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Arachidonic Acid Hydroperoxide; PE-AdA-OOH, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Adrenal Acid Hydroperoxide; PE-AA-OO., Phosphatidylethanolamine-Arachidonic Acid Peroxyl Radical; PE-AdA-OO., Phosphatidylethanolamine-Adrenal Acid Peroxyl Radical; PE-AA-OH, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Arachidonic Acid Alcohol; PE-AdA-OH, Phosphatidylethanolamine-Adrenal Acid Alcohol; Glu, Glutamic Acid; Cys, Cysteine; GSH, Glutathione; GSSG, Glutathione Disulfide; GPX4, Glutathione Peroxidase 4; ACOT2, acyl-CoA thioesterase 2; StAR, steroidogenic acute regulatory; PKCβII, protein kinase C βII.