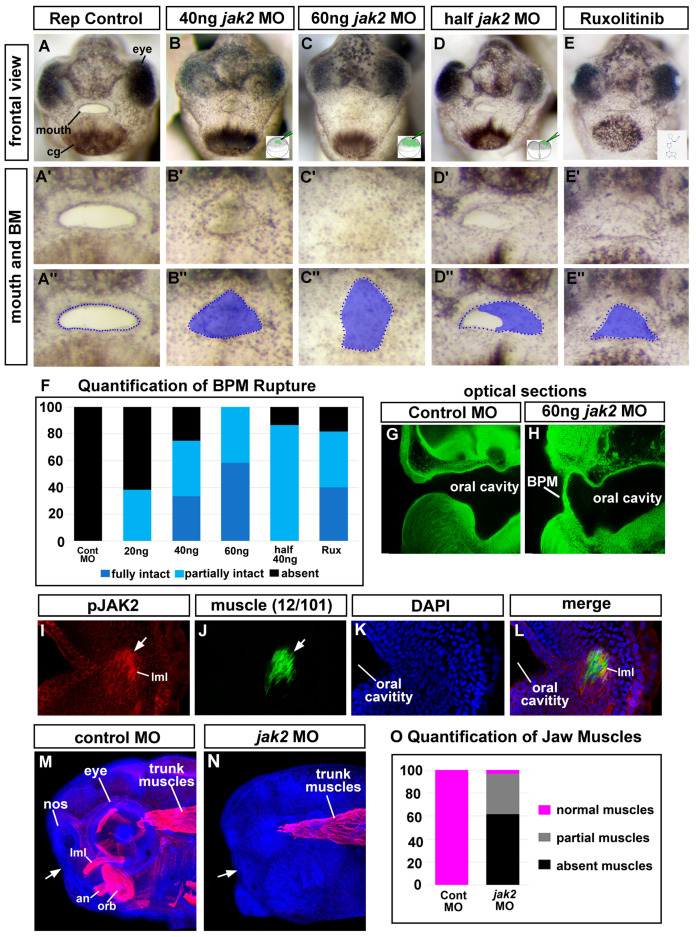
Figure 3.
Jak2 knockdown affects the buccopharyngeal membrane and cranial muscles. (A–E’’) Frontal view of the face of representative embryos at stages 40–41 showing ruptured or persisting buccopharyngeal membranes (images from n = 60, 3 biological replicates for each treatment). The bottom right corner shows an image of the injection site/stage. Prime-labeled images show magnified images of the mouth and the double-prime-labeled images show the same images with the buccopharyngeal membrane shaded in blue. (F) Shows relative percentages of embryos with an intact, partially intact, or absent buccopharyngeal membrane (n = 60 for each group, 3 biological replicates). (G,H) Optical sagittal section through the head of representative controls and jak2 morphants. The buccopharyngeal membrane is absent in the control and is present but thin in the jak2 morphants (n = 12, 2 biological replicates). (I–L) Representative thick agarose section through the face showing phosphor-‘JAK2 and 12/101 immunofluorescence. (I) phospho-Jak2 (red), (J) 12/101 = muscle-specific antibody (green), (K) DAPI (blue), (L) merge. (M,N) Lateral views of representative embryos showing 12/101 muscle labeling (red) in control and jak2 morphants and counterstained with DAPI (blue). White arrows point to the location of the mouth. (O) Quantification of the presence of cranial muscles in control and jak2 morphants (n = 60, 2 biological reps). Abbreviations; BPM = buccopharyngeal membrane, nos = nostril, MO = morpholino, levator mandibulae longus = lml, orbithyoidus = orb, angularis = an.