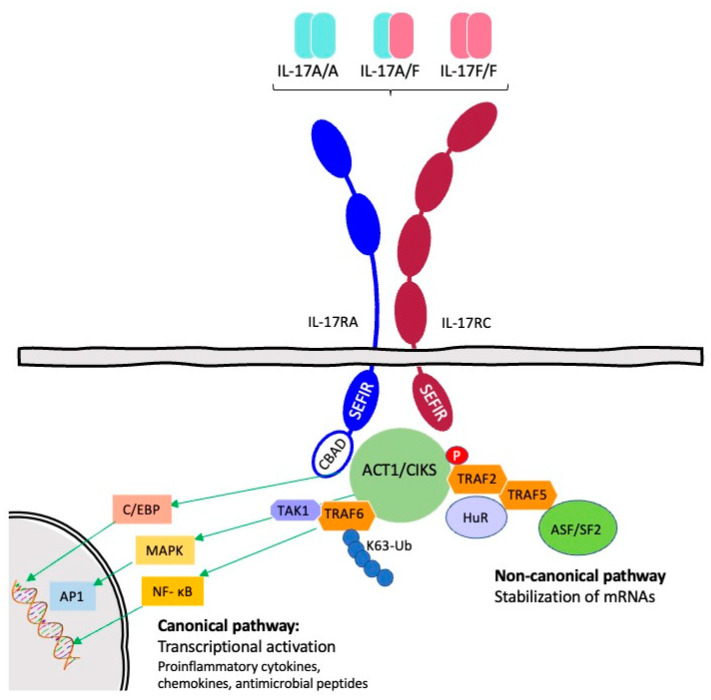
Figure 1.
IL-17RA/RC signalling pathways (Figure adapted from Monin and Gaffen [3], and from Chung [4]). Homotypic interactions between the SEF/IL-17R (SEFIR) domains of the receptor and the adaptor Act1/CIKS are made possible by ligand (IL-17A/IL-17F/IL-17A/F) binding to the receptor complex. The nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) route, the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein b (C/EBPb), and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways are all activated by the conventional IL-17 signalling pathway, which is started by Act1-induced K63 linked ubiquitination of TNF receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6). Downstream target genes, such as those encoding proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and antimicrobial peptides, are then transcriptionally activated as a result. In contrast, noncanonical signalling relies on Act1 phosphorylation at amino acid 311, leading to recruitment of the RNA-binding protein HuR and formation of the TRAF2/TRAF5 complex, which sequesters the alternative splicing factor ASF/SF2 (mRNA-destabilizing) [3,4].