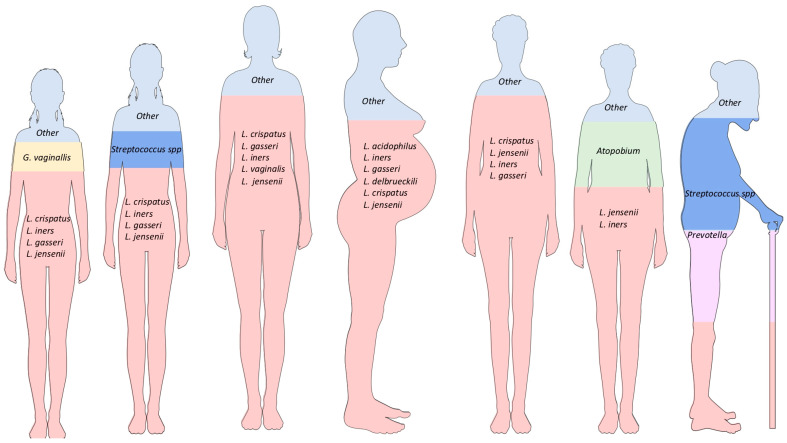
Figure 3.
Lifetime changes in women’s microbiota proportions. Due to changes in anatomy, physiology, and hormones during different life stages, women experience an evolution of resident microorganisms, creating a healthy environment during fertile stages. At the extremes of life, there is higher diversity in the microbiota, but some species can lead to the development of genitourinary conditions and proinflammatory states. The high levels of estrogen during the reproductive stage promote the healthy development of Lactobacillus spp., allowing for a balanced environment and protection against pathogens. During pregnancy, the dynamicity resulting from hormonal and anatomical changes promotes the growth of Lactobacillus spp. and other bacteria. The increasing diversity of Lactobacillus spp., including L. crispatus and L. jensenii, may protect the mother–child dyad during the perinatal period, preventing complications and providing nourishment during the gestational period.