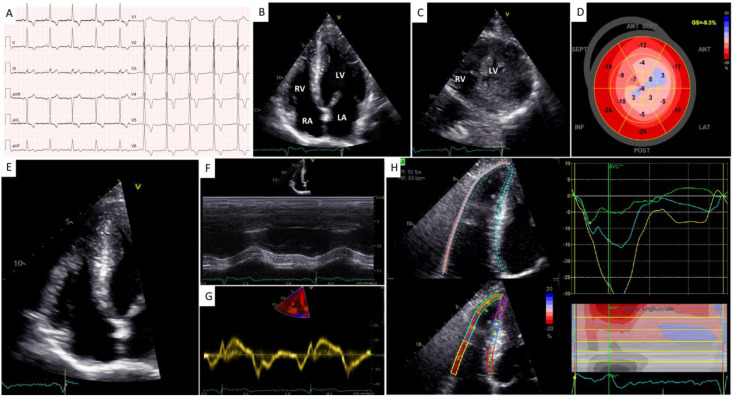
Figure 1.
Initial work-up with electrocardiography and transthoracic echocardiography. (A) A 12−lead electrocardiogram. (B) A 2−dimensional (2D) transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) 4−chamber apical view showing biventricular hypertrophy with an “ace of spades” morphology of the left ventricular (LV) cavity. (C) A 2D−TTE parasternal short-axis view at the level of the apex showing biventricular hypertrophy. (D) A 2D speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE) map showing reduced global longitudinal strain in the mid-apical segments of the left ventricle. (E) A 2D right ventricle (RV) −focused 4−chamber apical view. (F,G) Conventional indices of longitudinal RV systolic function, i.e., TAPSE (F) and S’ TDI (G). (H) A 2−D STE map showing reduced RV free wall longitudinal strain.