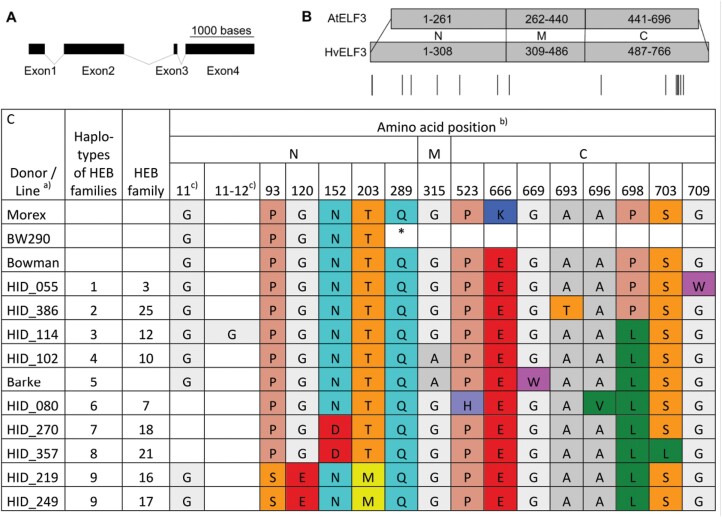
Fig. 4.
ELF3 protein structure and sequence polymorphisms. (A) Structure of the HvELF3 gene in barley (Barke). Exons are shown as black rectangles and introns as connecting lines. (B) Domain mapping and their sequence annotation between the Arabidopsis (Col-0) ELF3 protein (AtELF3) and Barke/Morex ELF3 protein (HvELF3). Numbers indicate amino acid positions of N-terminal (N), middle (M), and C-terminal (C) protein domains. Amino acids 696 and 766 are the STOP codons for AtELF3 and HvELF3, respectively. Lines beneath HvELF3 mark sites of amino acid substitutions and insertion or deletion between HIFs used in field trials (as indicated in C). (C) ELF3 protein sequence polymorphisms of all alleles present in the field trials, Morex, Bowman, and BW290. Only the amino acid positions with variation between the families are shown. One-letter amino acid abbreviations (JCBN, 1984) were used, and the asterisk shows a stop codon. A) HID=‘hordeum identity’; name of the donor accession. b) N, M, and C regions of barley ELF3 were obtained by alignment of the Barke/Morex sequence with the Arabidopsis sequence, and Barke/Morex/Bowman sequences were used as references for the amino acid positions. c) Between position 11 and 12 some lines have an insertion and at position 11 some lines have a deletion of one amino acid, compared with the Barke amino acid sequence.