FIGURE 3.
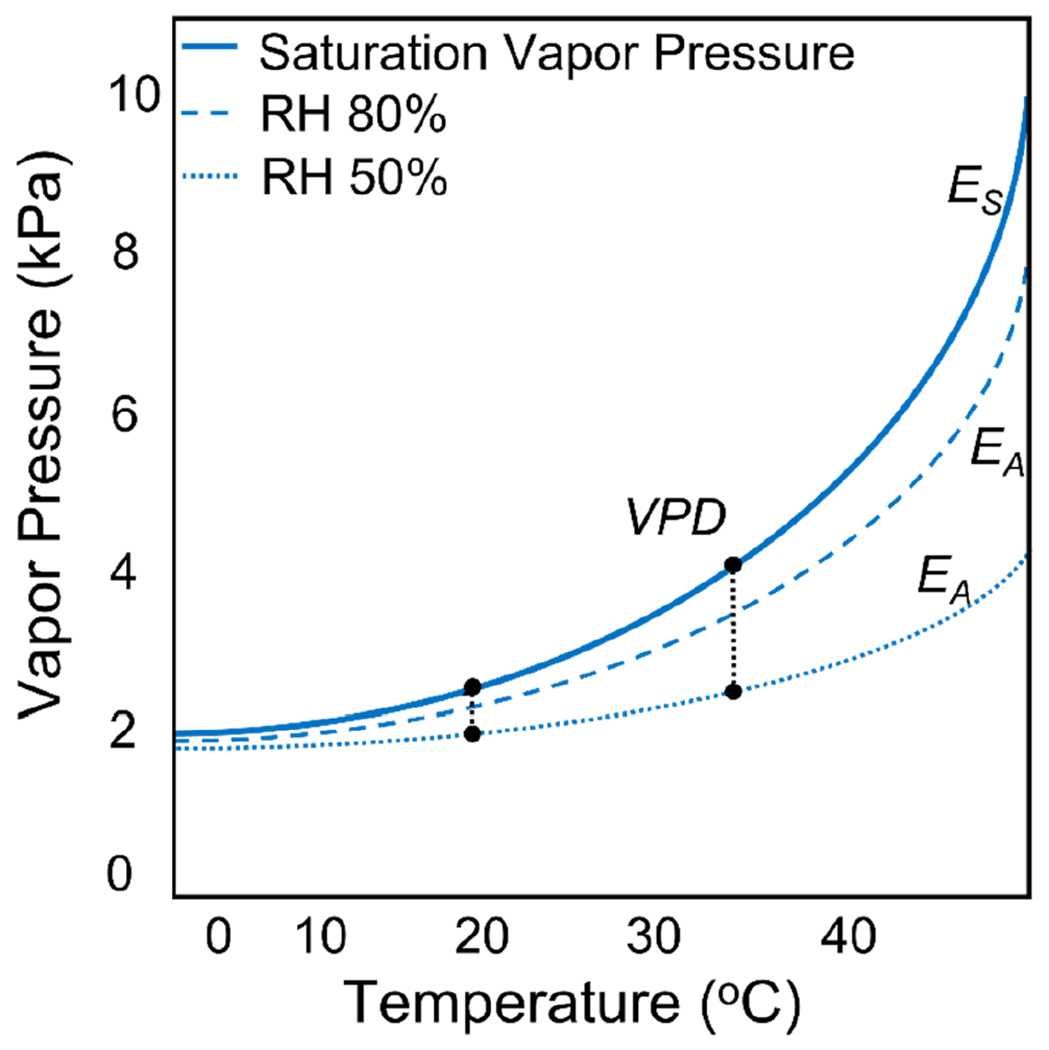
The total amount of water the air can hold, expressed here as saturation vapour pressure (Es), increases exponentially with temperature and is estimated as a function of temperature using the Tetens equation. The actual amount of water in the air, expressed here as vapour pressure (Ea), can be derived from relative humidity (RH) as Ea = RH/100 * Es. The vapour pressure deficit (VPD) is the absolute difference between Es and Ea and is an important metric of atmospheric moisture because it has a near linear relationship with evaporative potential. Thus, as temperature warms, for a given decrease in RH, there will be a larger increase in VPD and the amount of water stress mosquitoes experience.
