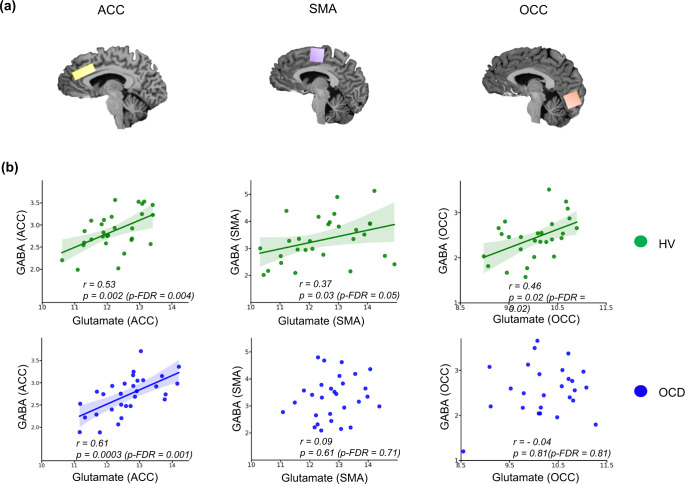
Fig. 1. Relationship between Glutamate and GABA in the anterior cingulate cortex, the supplementary motor area and the occipital cortex of the healthy and OCD brain.
The glutamate and GABA levels, expressed in parts per million (ppm), were measured in voxels placed in (a) anterior cingulate cortex (12 × 20 × 33 mm3), in yellow, supplementary motor area (20 × 20 × 20 mm3) in purple, and occipital cortex (20 × 20 × 20 mm3) in orange, of (b) healthy participants in green, and participants with OCD in blue. The line of best fit is shown with the 95% confidence intervals for the regression estimate in translucent bands around the regression lines. All metabolites were normalised using (Cr + PCr), corrected for grey and white matter and cerebral spinal fluid of each individual voxel, within subjects. For the ACC voxel the sample size for Glu and GABA in the OCD group was (n = 30) and in HV (n = 30). For the SMA voxel the sample size for Glu in the OCD group was (n = 31) and in the HV it was (n = 30), for GABA in the OCD group it was (n = 30) and in the HV the sample size was (n = 29). Lastly, for the OCC voxel the sample size for Glu in the OCD group was (n = 30) and in the HV it was (n = 28), for GABA in the OCD group it was (n = 27) and in the HV the sample size was (n = 29). All relationships were studies using a two-tailed Pearson test. The data for this figure are provided in the Source Data file. Acronyms: ACC anterior cingulate cortex, SMA supplementary motor area, OCC occipital cortex, GABA γ-amino-butyric acid, p-FDR p-value corrected for False Discovery Rates98, r Pearson’s r correlation coefficient, HV Healthy Volunteers, OCD Obsessive Compulsive Disorder.