Figure 5. MAP4K4 localizes at cell–cell junction, in a CNH-dependent manner, and both CNH domain and kinase activity are necessary for MAP4K4 role.
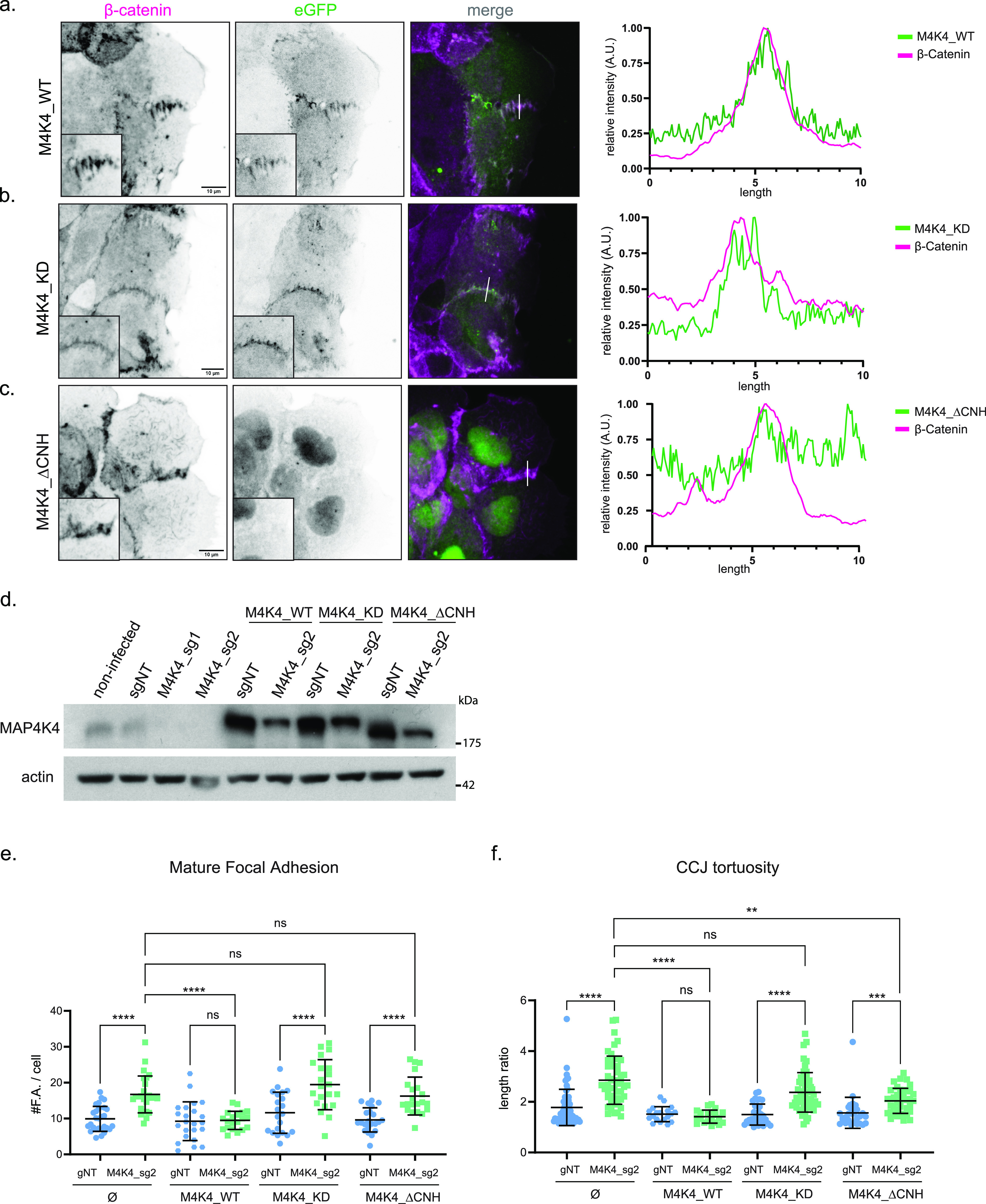
(A, B, C) z-scan projection of representative confocal images of β-catenin stained A431 clusters, stably expressing (A) eGFP–MAP4K4_WT, (B) eGFP–MAP4K4 kinase dead (MAP4K4D153N), or (C) deleted for the CNH domain (MAP4K4ΔCNH). Line scan indicates the colocalization between β-catenin and MAP4K4. (D) Immunobloting of MAP4K4 or actin for lysates of A431 cells controls (non-infected or sgNT), KO for MAP4K4 (sg_1 or sg_2) alone or expressing eGFP–MAP4K4 WT, KD, or ΔCNH, resistant to sg_2. (E) Number of zyxin-positive focal adhesions for A431 clusters control (sgNT) or KO for MAP4K4 (M4K4_sg2) and stably expressing eGFP–MAP4K4 WT, KD, or ΔCNH, resistant to sg_2. (F) Cell–cell junction tortuosity index for A431 clusters control (sgNT) or KO for MAP4K4 (M4K4_sg2), and stably expressing eGFP–MAP4K4 WT, KD, or ΔCNH, resistant to sg_2. Data on (E, F) are represented as mean ± s.d. and tested by Kruskal–Wallis (ns, nonsignificant; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001).
