Figure 2.
Classification and multi-omics integration of retinal cell types
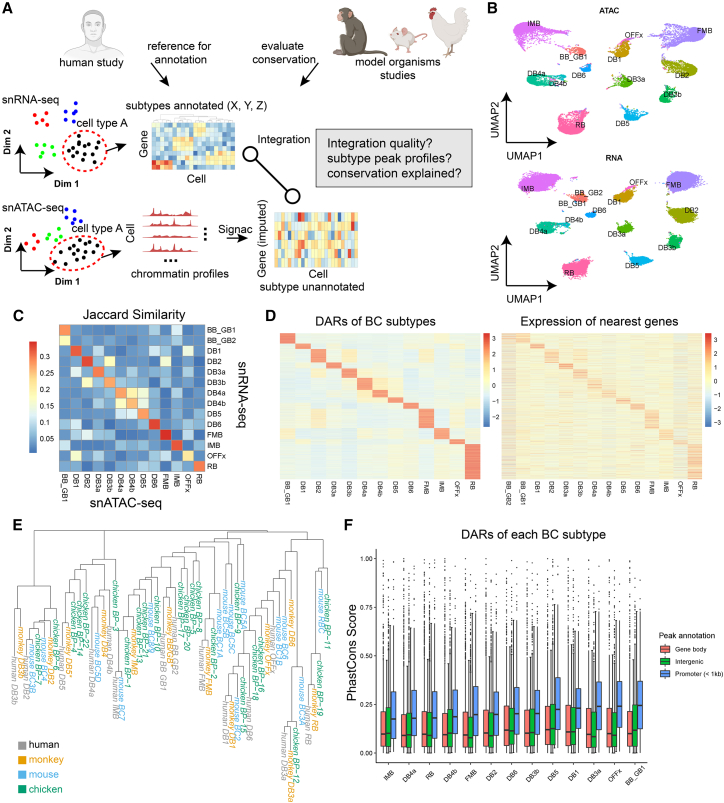
(A) The analysis strategy to perform classification and multi-omics integration of retinal cell types. We perform sub-clustering solely using snRNA-seq data first and leverage published single-cell RNA-seq data of human or model organisms to assist the annotation of the cell types. We then annotate the snATAC-seq data using the annotated snRNA-seq data as the reference.
(B) Two-dimensional embeddings (UMAP) for bipolar cells of the ATAC (top) and RNA (bottom) modality.
(C) Heatmap representing the similarity between the differentially expressed genes and the differentially accessible genes from each bipolar cell type.
(D) Demonstration of the consistency between the differentially accessible regions (DARs, left) and their nearest genes (right) among bipolar cell types.
(E) Phylogenetic tree representing the overall similarity of bipolar cell types among four species: human (gray), monkey (yellow), mouse (blue), and chicken (green).
(F) Boxplot showing the PhastCons score of DARs of each bipolar cell type. The DARs were partitioned to “gene body,” “intergenic,” or “promoter” before the visualization. The center line of the boxplot shows the median of the data; the box limits show the upper and lower quartiles; the whiskers show 1.5 times interquartile ranges.