Figure 1.
Gene expression levels consistently delineate cell type and show differences between AS patients and HCs
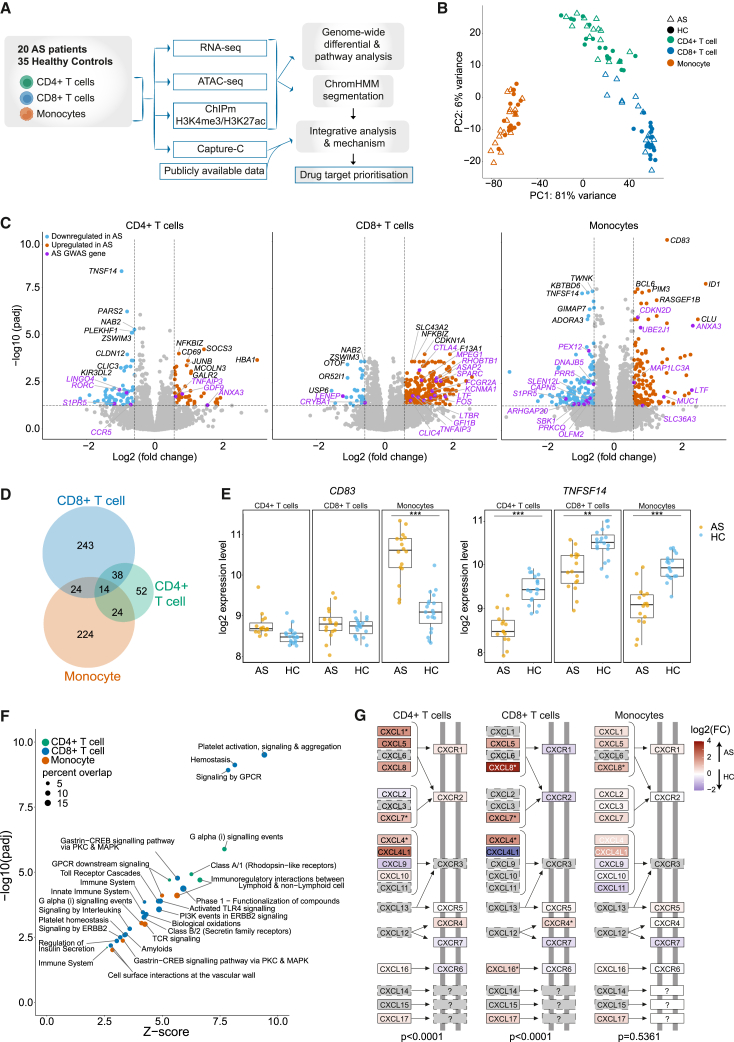
(A) Workflow of the study.
(B) PCA of RNA-seq data in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and monocytes from AS patients and HCs.
(C) Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes calculated using DEseq2 (padj < 0.05, FC > 1.5) between AS patients and HCs in CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, and monocytes. Genes in AS-associated GWAS regions are purple. Red genes are upregulated and blue downregulated in AS patients. CD4+ T cells had 122 differentially expressed genes, CD8+ T cells 299 genes, and monocytes 300 genes.
(D) Cell type specificity of differentially expressed genes; numbers of differentially expressed genes are given.
(E) Examples of differential gene expression at CD83 and TNFSF14; ∗∗padj < 0.01, ∗∗∗padj < 10−7 (from DEseq2).
(F) Enriched pathways in the Reactome database (FDR < 0.01 from XGR output) from significant differentially expressed genes in each cell type. Dot size represents percentages of genes represented in that pathway, and colors represent cell types.
(G) CXC subfamily of the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) “cytokine-cytokine reception interaction” pathway colored by gene expression log2 FC. Significantly differentially expressed genes are marked by asterisks. The p value of CXC family subset over-representation is shown below for each cell type, calculated by chi-squared test with Yates’ correction.