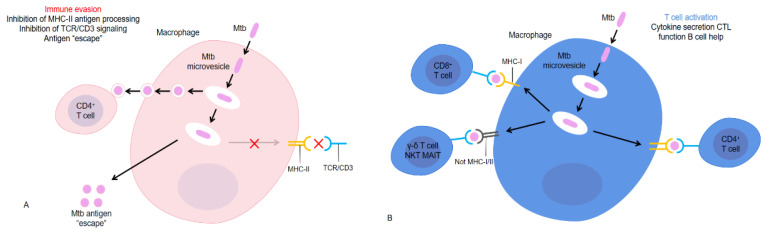
Figure 3.
Evasion of T cell recognition versus T cell activation by Mtb-infected antigen-presenting cells. The paradox of T cell responses to Mtb is that, on the one hand, (A) Mtb antigens, when properly processed by activated antigen-presenting cells, elicit a broad range of T cell responses in LTBI-diseased animals. This involves many T cell subsets responding to various antigens. These MTB-activated T cells mainly secrete Th1 cytokines and chemokines, have cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) functions, and help B cells. On the other hand, (B) Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which is sheltered by macrophages, can use several mechanisms to interfere with T cell recognition.