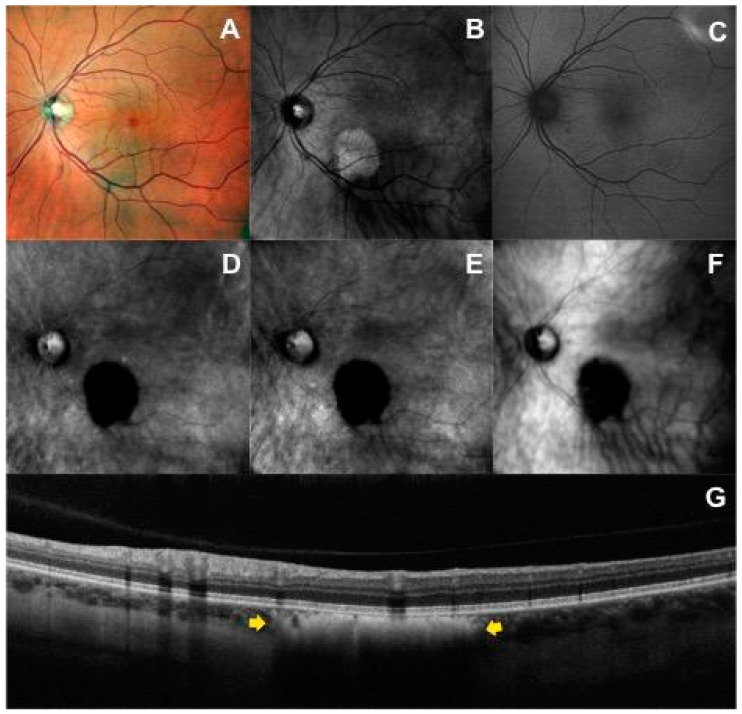
Figure 2.
Multimodal imaging of a patient with choroidal nevus in the left eye: (A) Multicolor fundus image shows a lightly and heterogeneous pigmented area with barely visible lesion borders localized inferior to the fovea. (B) Infrared image shows a hyperreflective mass. (C) On the green fundus autofluorescence image, the nevus is not visualized. Left-deviated (D) and right-deviated (E) retromode images show the characteristic hypo-retro-reflective pattern within the choroidal nevus characterized by a dense dark shadow with sharp margins, shared also with dark-field mode (F). (G) The horizontal optical coherence tomography scan passing through the lesion identifies the choroidal nevus (yellow arrows) as a flat hyperreflective lesion with posterior shadowing, an intact overlying retinal pigment epithelium, and intact outer retinal layers.