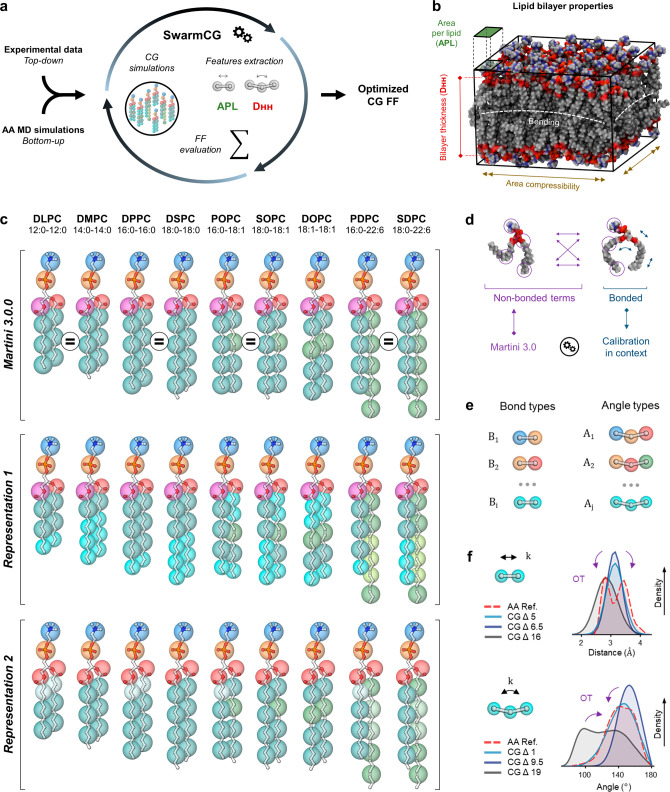
Figure 1.
Overview of the protocol followed for obtaining bonded parameters via SwarmCG for different CG models of lipids within the framework of Martini 3.0.0. (a) SwarmCG simultaneously relies on bottom-up and top-down references to iteratively optimize model parameters using higher-resolution AA MD simulations and experimental data. (b) Illustration of lipid bilayer properties showing notably the APL and DHH used for calculating the top-down component of the loss function. (c) Overview of the CG representations of interest in this study with CG beads mapping shown over AA structures using beads Q1 (dark blue), Q5 (orange), SN4a (red), N4a (purple), C1 (blue), SC2 (cyan), SC1 (white), C4h (olive), C5h (light green), and SC4h (bright yellow/green). SOPC is left out of the optimization procedures and used as part of the posterior evaluations. (d) Principle of the parameters calibration in this study: bonded parameters of the models are calibrated in the context of nonbonded interaction terms set to Martini 3.0.0, thereby iterating CG MD simulations of bilayers composed of different types of lipids. (e) CG bonds and angles are defined as building blocks and classified according to the CG beads they involve, which defines the type of a specific bond/angle, as well as the parameters employed. (f) Principle of the OT-B metrics used for exploiting structure-based information from AA reference simulations.