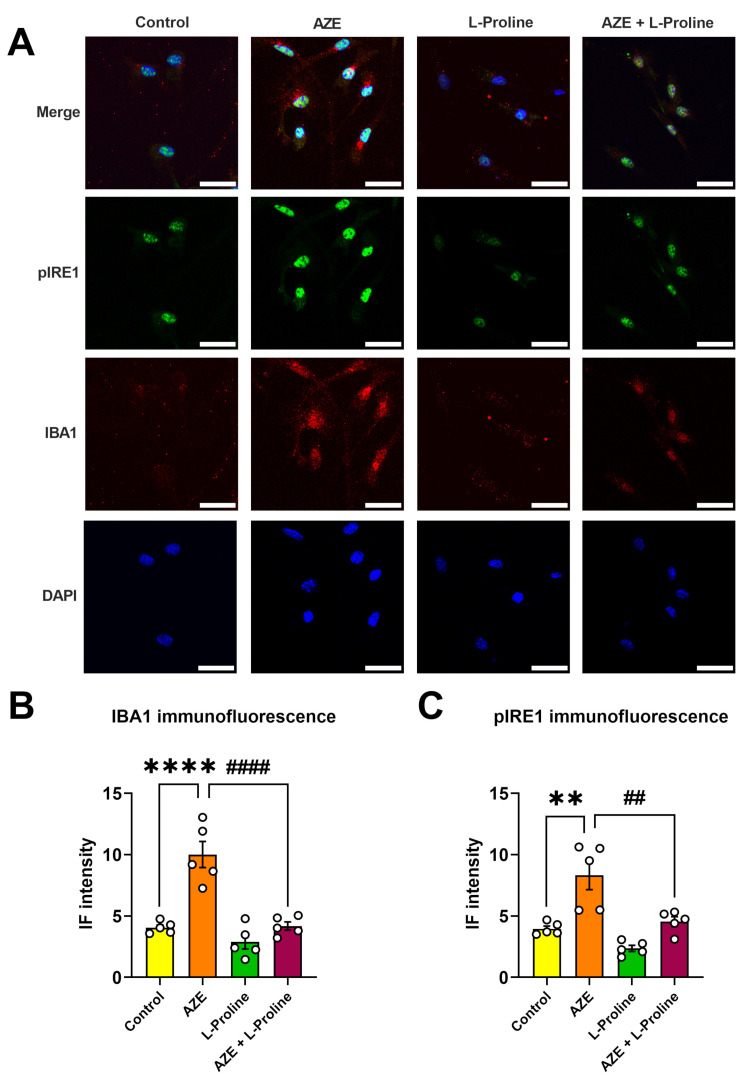
Figure 6.
AZE-induced IBA1 and phospho-IRE1Ser724 (pIRE1) expression is prevented by L-proline co-administration in primary microglial cells. (A) Representative photomicrographs showing pIRE1 and IBA1 co-immunofluorescence (co-IF) and (B,C) related quantifications of untreated primary microglia (control) or following exposure to AZE (1000 µM), L-proline (50 µM) or their combination after 24 h. Images were taken on a Leica Stellaris 8 confocal fluorescence microscope (Leica Microsystems) using the 63.5× oil-immersed objective. Scale bar = 20 µm. (B) IBA1 and (C) pIRE1 IF intensities were determined using NIH ImageJ software, ver. 1.52. At least five independent images from independent experiments were quantified for each experimental condition (n = 5). Results shown are the mean ± SEM. ** p < 0.01 or **** p < 0.0001 vs. control; ## p < 0.01 or #### p < 0.0001 vs. AZE, as determined using a one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey post hoc test. Aze = L-azetidine-2-carboxylic acid; IBA1 = ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1; pIRE1 = phospho-inositol-requiring transmembrane kinase/endoribonuclease 1αSer724; DAPI = 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (nuclear dye).