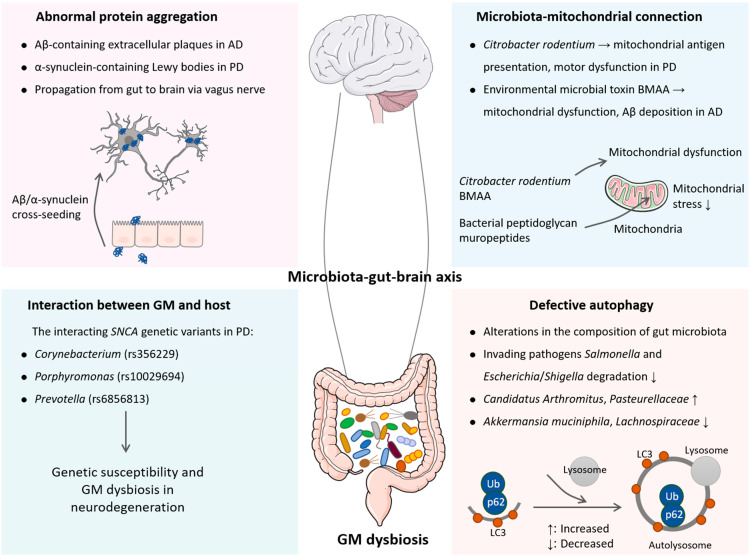
Figure 1.
Potential mechanisms of gut microbiome dysbiosis involved in neurodegenerative diseases. AD is characterized by Aβ-containing extracellular plaques, and PD is characterized by intracellular α-synuclein accumulation to form Lewy bodies. The propagation of Aβ and α-synuclein in the gastrointestinal tract can be transmitted via the vagus nerve to the brain. In addition, there is an interaction between host genetic susceptibility to neurodegeneration and GM dysbiosis, that is, Corynebacterium, Porphyromonas, and Prevotella interact with the SNCA genetic variants rs356229, rs10029694, and rs6856813, respectively. Citrobacter rodentium and environmental microbial neurotoxin BMAA trigger mitochondrial dysfunction, ultimately leading to neurodegeneration. Furthermore, defective autophagy fails to eliminate intracellular pathogens and induces alterations in the composition of the gut microbiome.