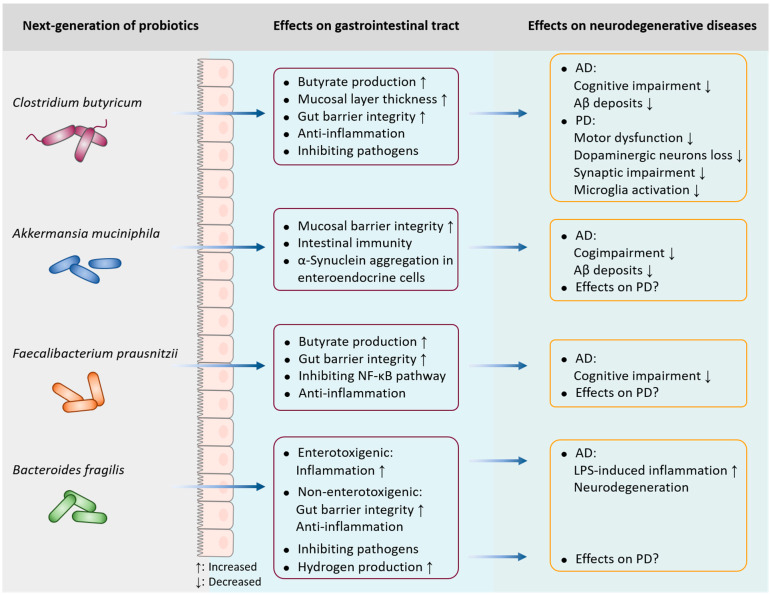
Figure 2.
Implications of new probiotics in neurodegenerative diseases. Clostridium butyricum, a butyrate-producing anaerobic bacterium, plays a protective role in neurodegenerative diseases; it can prevent cognitive impairment and Aβ deposits in AD, and improve motor deficits, dopaminergic neuron loss, synaptic dysfunction, and microglial activation in PD. Akkermansia muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii are effective in alleviating cognitive deficits and reducing Aβ levels in AD; however, their potential role in PD is unclear. Additionally, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis drives LPS-induced inflammation and degenerative neuropathology in AD, while non-enterotoxigenic B. fragilis exerts anti-inflammatory properties. Although B. fragilis accounts for the level of intestinal hydrogen in PD, its exact role in the neurodegeneration of PD has not yet been elucidated.