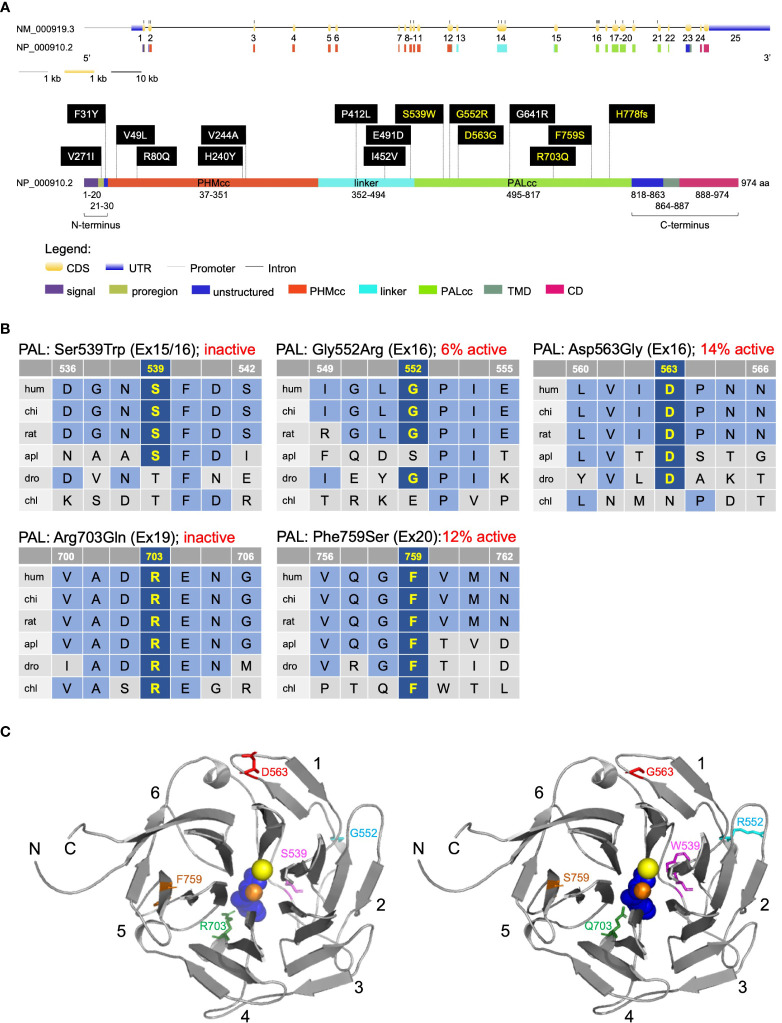
Figure 2.
Location and evolutionary conservation of the missense and frameshift PAM SNVs that were functionally tested. (A) Schematic representation of the PAM gene (GenBank: NM_000919.3, PAM-1, 25 exons) and encoded protein (NP_000910.2, 974 amino acids), including functional domains, with 15 missense and one frameshift SNVs. Gene and protein structures were drawn with the Gene Structure Display Server (GSDS ver. 2.0) (12). Variants found to have deleterious effects on PAM function/expression (p < 0.01) are shown in yellow lettering, while those without major effects are shown in white lettering. Brackets identify the non-catalytic regions that precede PHMcc (N-terminus) and follow PALcc (C-terminus); CD, cytosolic domain; CDS, coding sequence; PALcc, catalytic core of peptidyl-α-hydroxyglycine α-amidating lyase; PHMcc, catalytic core of peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase; TMD, transmembrane domain; UTR, untranslated region. (B) Protein sequence alignments for five of the variants with deleterious effects. Conserved affected residues are shown in yellow. PAL activities, indicated in red, refer to functional experiments in PEAKrapid cells. (C) The crystal structure of rat PALcc (PDB entry 3FW0) was used to contextualize the missense variants categorized as likely pathogenic based on in silico analyses; the WT residue is shown on the left and the mutant residue on the right. PAL folds as a β-propeller, with six blades (numbered 1–6) positioned around a central cavity. The calcium and mercury ions are depicted as yellow and orange spheres, respectively. The mercury ion was used instead of zinc to capture the binding of a non-peptide substrate, α-hydroxyhippuric acid, depicted in blue. The affected residues are highlighted in purple (Ser or Trp 539), cyan (Gly or Arg 552), red (Asp or Gly 563), green (Arg or Gln 703), and orange (Phe or Ser 759), along the ribbon visualization of WT rat PALcc in gray. Arg703 is positioned at the active site and participates in substrate binding. Interestingly, p.Gly552Arg and p.Asp563Gly are located on the same face of the β-propeller. C, C-terminus; N, N-terminus.