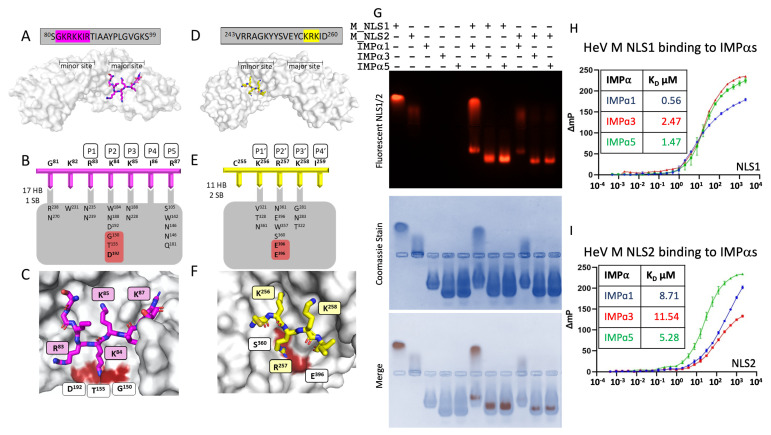
Figure 2.
Structural basis for the interaction between the matrix putative NLS sequences and IMPα. (A) HeV M NLS1 peptide sequence displayed in grey box with resolved amino acids highlighted in magenta. Matrix NLS1 (magenta sticks) binds to IMPα (grey surface) at the major site. (B) Schematic of the interface between NLS1 (magenta) and IMPα (grey). HeV M K84 binds to P2 site on IMPα (Gly150, Thr155, and Asp192) (highlighted red) with H-bonds and salt bridge interactions depicted. (C) The resolved amino acids of HeV M NLS1 (magenta sticks) are shown in the major binding site of IMPα. (D) HeV M NLS2 peptide sequence displayed in the grey box with resolved amino acids highlighted in yellow. Matrix NLS2 (yellow sticks) binds to IMPα (grey surface) at the minor site. (E) NLS2 binds to IMPα as a non-classical, minor-site only NLS. Schematic of the interface between NLS2 (yellow) and IMPα (grey). Hydrogen bonds are shown in standard font, and salt bridges in bold font. (F) The resolved amino acids of HeV M NLS2 (yellow sticks) are shown in the minor binding site of IMPα, with R257 forming salt bridges with Glu396 and Ser257 (highlighted in red). (G) Electromobility shift assay (EMSA) showing NLS1 in lane 1, NLS2 in lane 2, IMPα1, 3, and 5 in lanes 3, 4, and 5, respectively. NLS1 combined with IMPα1, 3, and 5 in lanes 6–8, respectively, and NLS2 combined with IMPα1, 3, and 5 in lanes 9–11, respectively. (H,I) Fluorescence polarization assays measuring binding strength between NLS1 and NLS2 of HeV and NiV M proteins respectively.