Figure 4. S. aureus and CoNS that do not produce antibiotic activity are more resistant to AMPs.
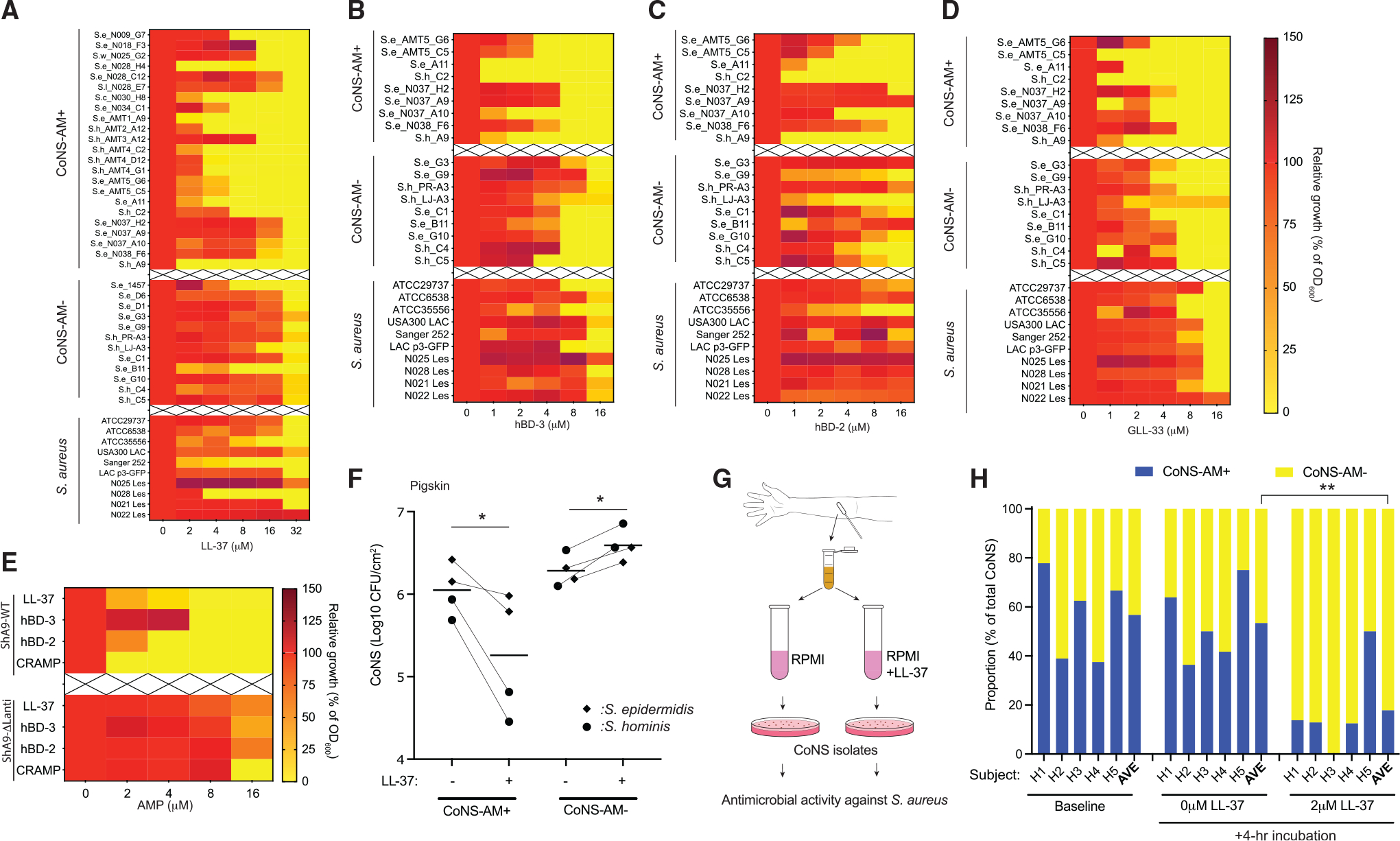
(A–D) Dose-dependent growth inhibition of representative strains of antimicrobial CoNS (CoNS-AM+), non-antimicrobial CoNS (CoNS-AM−), and S. aureus by human cathelicidin LL-37 (A), hBD-3 (B), hBD-2 (C), and mouse cathelicidin GLL-33 (D). Se, S. epidermidis; Sh, S. hominis; Sl, S. lugdunensis; Sc, S. capitis; Sw, S. warneri. Data represent mean of duplicate technical replicates.
(E) Comparison of growth inhibition of ShA9-WT and a ShA9-ΔLanti by human and murine AMPs. Growth of bacteria was monitored by OD600, and scale of relative growth was shown by heatmap (A–E). Data represent the mean of duplicate technical replicates.
(F) Effects of LL-37 on colonization by representative CoNS-AM+ or CoNS-AM− strains of S. epidermidis or S. hominis on pigskin sheet for 24 h. Each dot represents the average of duplicate technical replicates from an individual bacterial strain, and the horizontal bar represents the mean of 4 distinct bacterial strains. p value (*p < 0.05) was calculated by two-tailed unpaired parametric t test.
(G and H) Effect of a low dose of LL-37 on the proportion of CoNS-AM+ and CoNS-AM− within the microbial community on the forearm skin of healthy human subjects in vitro. p value (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001) was calculated by two-tailed paired parametric t test.
