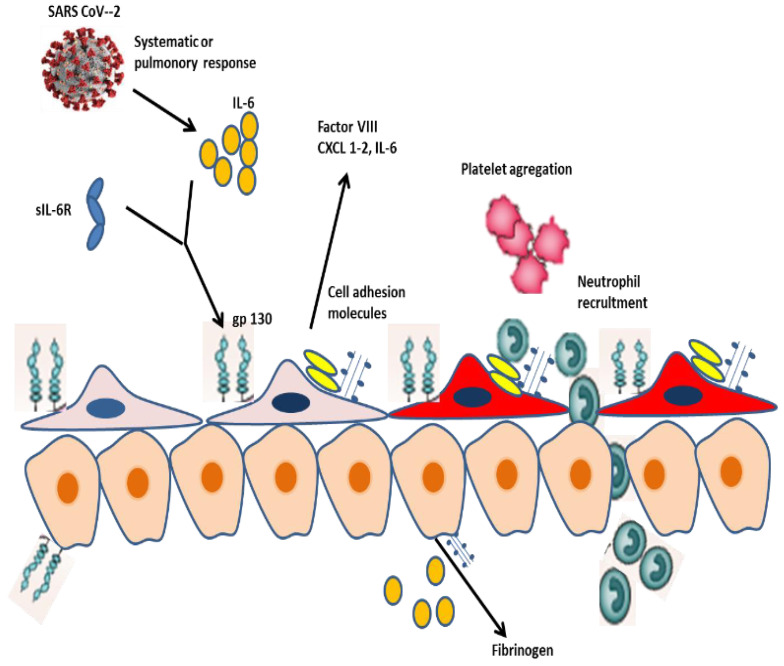
Figure 2.
LSEC activation and cellular interaction during SARS-CoV-2 infection. SARS-CoV-2 infection stimulates a systemic release of IL-6 that induces LSECs through a trans-signaling pathway involving the sIL-6R and gp130. Activated LSECs acquired a procoagulant and proinflammatory phenotype, which express vWF, Factor VIII, CXCL1, and 2 and cell adhesion molecules, which eventually promote platelet and neutrophil recruitment in the liver. Additionally, LSECs express IL-6 and interact with hepatocytes, which respond to IL-6 through a classical signaling pathway involving the IL-6R. Hepatocytes play a critical role in the systemic response to SARS-CoV-2 via expressing fibrinogen and acute phase proteins.