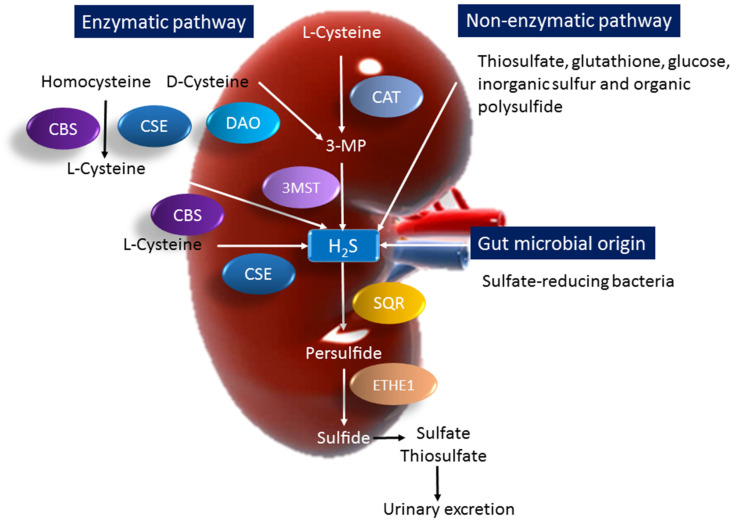
Figure 2.
Three major H2S synthesis pathways are of enzymatic, non-enzymatic, and gut microbial origin. Cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) or cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) catalyzes homocysteine to produce l-cysteine. Both CBS and CSE can catalyze l-cysteine to generate H2S. 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (3MST) produces H2S from 3-mercaptopyruvate (3-MP), which is formed by d-amino acid oxidase (DAO) cysteine aminotransferase (CAT) from d-cysteine and l-cysteine. Another source of endogenous H2S is derived from the non-enzymatic synthesis pathway. The other source of H2S comes from intestinal bacteria, mainly from sulfate-reducing bacteria. H2S is metabolized by sulfide quinone oxidoreductase (SQR) to form persulfide, which can be oxidized by persulfide dioxy-genase (ETHE1) to yield sulfite. Sulfite is converted to sulfate or thiosulfate, which can be excreted into the urine.