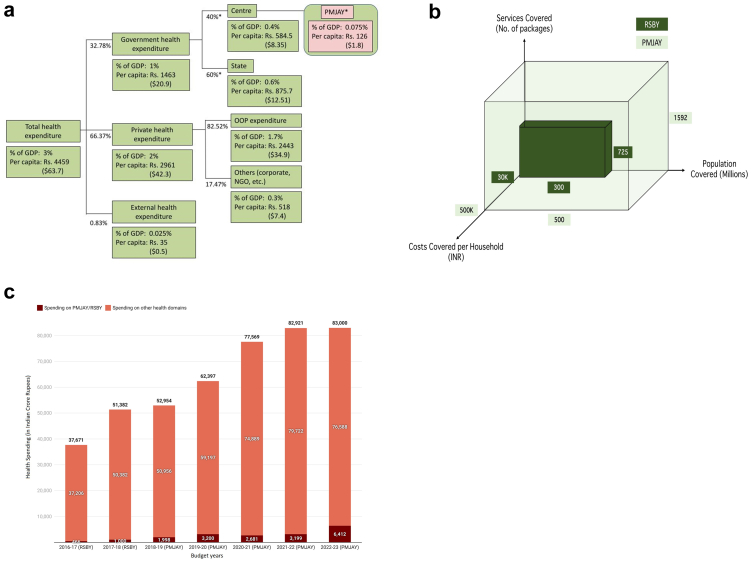
Fig. 1.
Financing of health system and GFHIS in India. (a) Sources of healthcare financing in India, (b) Universal health coverage (UHC) Cubes: RSBY vs PMJAY, (c) Central Government spending on PMJAY/RSBY scheme and other health domains (in crore Indian Rupees). GDP: Gross Domestic Product, PMJAY: Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, RSBY: Rashtriya Swasthya Bima Yojana, OOP: Out-of-pocket, NGO: non-government organization. In figure (a), values for various sources of health expenditure were taken from World Bank 2019 and ∗ indicates authors' calculation. GDP of India was Rs. 198 lakh crore and the population was 136 crore in 2019 @ 1$ = Rs. 70.4. External health expenditure is the share of total health expenditure funded from outside the country (foreign source). In figure (c) values of central government spending is taken from Union Budget of India. For year, 2021-22 spending values indicate budget estimates, for 2020-21 spending values indicate revised estimates, and for the rest of the years spending values indicate actual spending.