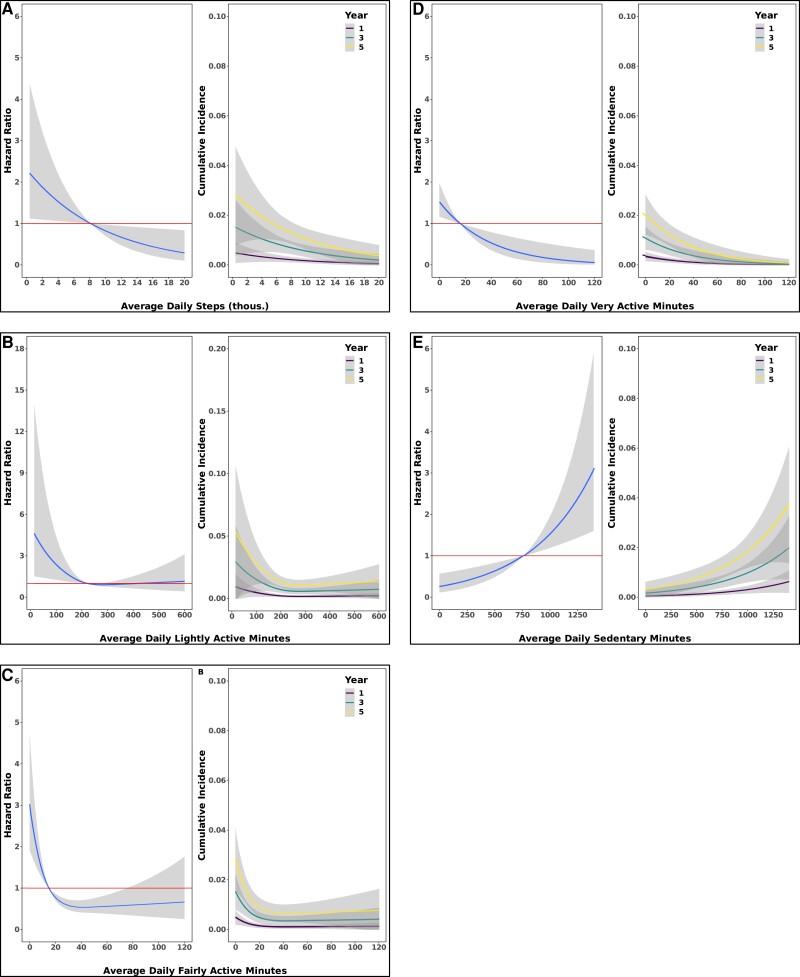
Figure 5.
Greater amounts of physical activity are associated with lower risk for incident type 2 diabetes mellitus. Spline curves demonstrating the hazard ratio and 95% CI for incident type 2 diabetes mellitus as a function of measures of physical activity (left figures). Spline curves demonstrated the cumulative incidence and 95% CI for type 2 diabetes mellitus as a function of measures of physical activity (right figures). (A) daily steps (B) lightly active minutes (C) fairly active minutes (D) very active minutes (E) sedentary minutes. Data come from Cox regression models adjusted for age, sex, race, and body mass index.