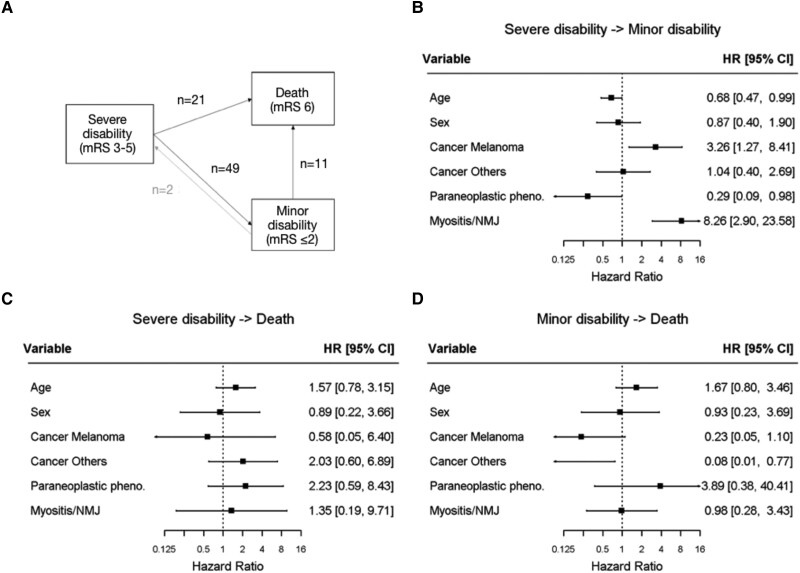
Figure 4.
Presentation of the multi-state Markov model and multivariate analysis of outcomes. Each patient was categorized into one of three different states of disease at onset, 6 months, 12 months and 18 months: minor disability (mRS ≤2), severe disability (mRS 3-5), and death (mRS = 6); the transition rates from severe disability to a minor disability, severe disability to death and minor disability to death across these time points were estimated using maximum likelihood (A). Exposures were introduced into the different transitions to study their effects; forest plots showing the hazard ratios and confidence intervals according to the multivariate analysis for transition rates from severe disability to minor disability (B), severe disability to death (C) and minor disability to death (D), are represented. Melanoma and myositis/NMJ disorders were independently associated with a transition from severe to minor disability while increasing age and paraneoplastic-like syndromes independently decreased the rate of transition from severe to minor disability. Meanwhile, the transition rate from minor disability to death was decreased in patients with cancers other than lung and melanoma, compared to lung cancer. Abbreviations: CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; mRS = modified Rankin scale; NMJ = neuromuscular junction.