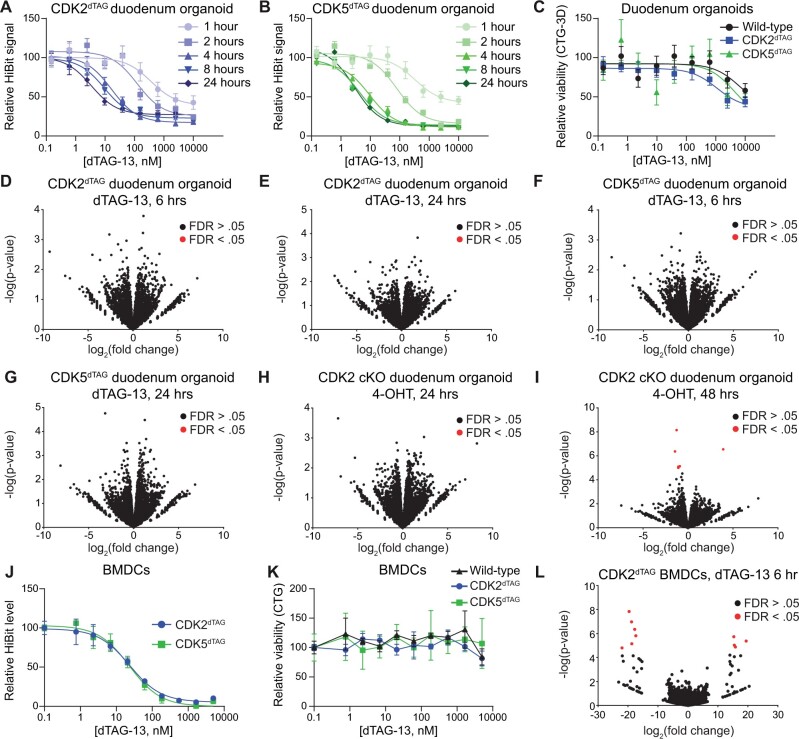
Figure 2.
Kinetics and consequences of CDK2 or CDK5 destruction using in vitro models of the bone marrow and small intestine. A and B, Kinetics of CDK2 or CDK5 destruction after dTAG-13 administration in duodenum organoids derived from HOM CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG mice. HOM CDK2dTAG (A) and HOM CDK5dTAG (B) duodenum organoids were treated as indicated and then the HiBit assay was performed to determine the amount of CDK2 (A) or CDK5 (B) protein. Values shown are normalized to DMSO treatment and are averages ± standard error of the mean (SEM) for 3 biological replicates. C, Degradation of CDK2 or CDK5 in CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG duodenum organoids does not affect viability. Duodenum organoids derived from WT, CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG HOM mice were treated with dTAG-13 for 4 days, then viability was measured by CellTiter-Glo 3D. Values shown are normalized to DMSO treatment and are averages ± SEM for 3 biological replicates. D and E, No significant changes in gene transcription after degrading CDK2 in CDK2dTAG duodenum organoids. Duodenum organoids derived from HOM CDK2dTAG mice were treated for 6 h (D) or 24 h (E) with 250 nM dTAG-13 or DMSO, QuantSeq was performed, and differential gene expression analysis was performed between the 2 groups. n = 3 biological replicates. FDR, false discovery rate. F and G, No significant changes in gene transcription after degrading CDK5 in CDK5dTAG duodenum organoids. Duodenum organoids derived from HOM CDK5dTAG mice were treated for 6 h (F) or 24 h (G) with 250 nM dTAG-13 or DMSO, QuantSeq was performed, and differential gene expression analysis was performed between the 2 groups. n = 3 biological replicates. (H and I) No significant changes in gene transcription after CDK2 KO in CDK2 cKO duodenum organoids. Duodenum organoids derived from HOM CDK2 cKO mice were treated for 24 h (H) or 48 h (I) with 1 µM 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) or DMSO, QuantSeq was performed, and differential gene expression analysis was performed between the 2 groups. n = 3 biological replicates. J, Potent degradation of CDK2 or CDK5 in BMDCs from CDK2dTAG and CDK5dTAG mice. Bone marrow cells were derived from multiple CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG HOM mice, pooled, treated with dTAG-13 in vitro for 6 h at the indicated concentrations, and the HiBit assay was performed to determine levels of CDK2 or CDK5 protein. Values are normalized to DMSO treatment and are averages ± SEM for 3 technical replicates. K, No change in viability after degrading CDK2 or CDK5 in BMDCs from CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG mice. Bone marrow cells were derived from 3–4 WT, CDK2dTAG or CDK5dTAG HOM mice, pooled, treated with dTAG-13 in vitro for 4 days at the indicated concentrations, and cell viability measured via CellTiter-Glo. Values are normalized to DMSO treatment and are averages ± SEM for 3 technical replicates. L, No significant changes in gene transcription after degrading CDK2 in BMDCs from CDK2dTAG mice. BMDCs from HOM CDK2dTAG were treated with 250 nM dTAG-13 or DMSO for 24 h, QuantSeq was performed, and differential gene expression analysis was performed between the 2 groups. n = 3 technical replicates. BMDCs, bone marrow derived cells.