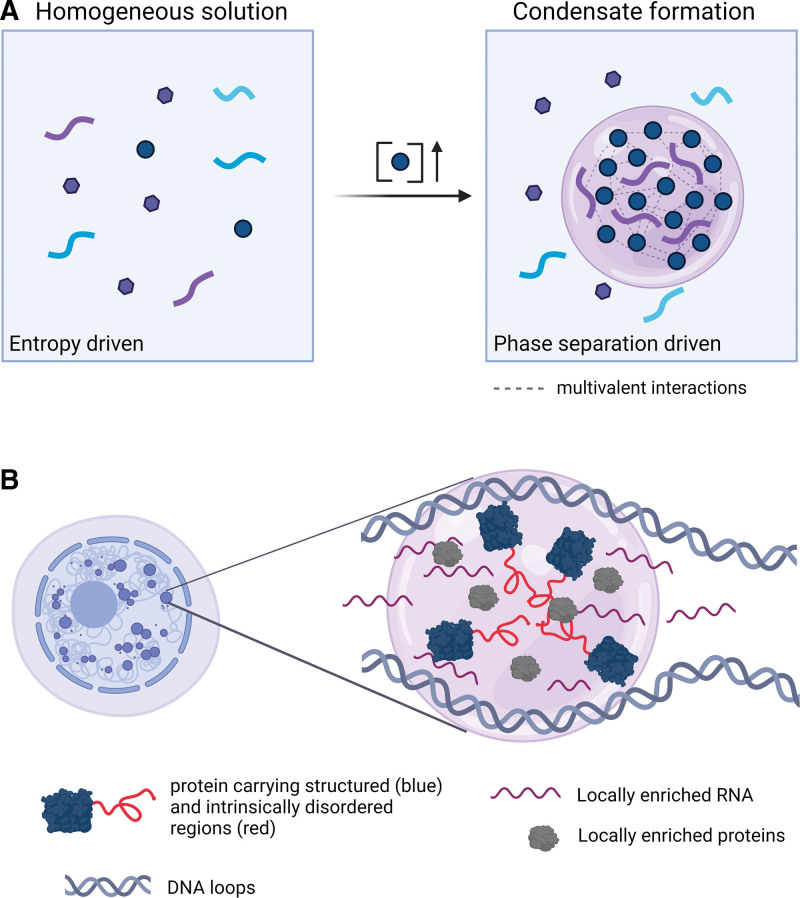
Figure 1.
Schematic representation and functions of phase separation in vitro and in vivo. (A) In an entropy-driven homogeneous solution, different molecular species remain dispersed. If one (or more) of the species reaches a critically high concentration, it becomes more thermodynamically favorable for these molecules to segregate into a phase-separated condensate. (B) Within cells, multivalent associations between proteins carrying IDRs induce high local concentration of factors that compose membrane-less subcellular compartments. In the nucleus, proteins, RNAs, and DNA interact to form these functional subcompartments. IDRs = intrinsically disordered regions.