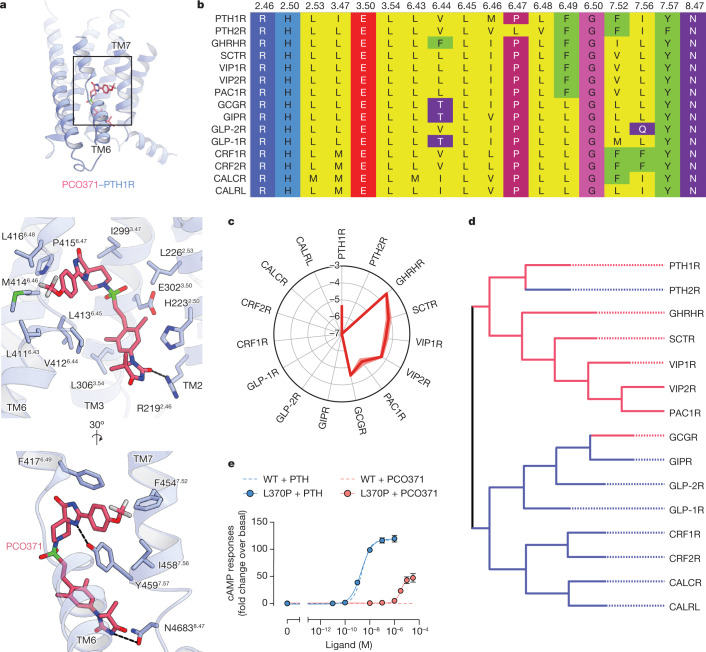
Fig. 4. PCO371 activates nearly half of class B1 GPCRs.
a, TMD region of PCO371-bound PTH1R (top) and magnified view of the PCO371-binding region (middle and bottom). b, Amino acid sequence alignment of human class B1 GPCRs. Described residues interact with PCO371. c, PCO371-induced GloSensor cAMP responses among class B1 GPCRs. Values in the radar chart indicate the logarithmic values of relative intrinsic activity (∆log RIAPCO-peptide), which is defined as the Emax/EC50 value (RIAPCO) in each receptor normalized by the Emax/EC50 value following stimulation by its endogenous peptide agonists (RIApeptide). Lines and shaded regions represent the means and s.e.m., respectively, of three independent experiments with each performed in duplicate. Note that in eight PCO371-insensitive GPCRs (PTH2R, GIPR, GLP-2R, GLP-1R, CRF1R, CRF2R, CALCR and CALRL), the RIAPCO values could not be calculated. Therefore the ∆log RIAPCO-peptide values are denoted as less than −7. d, Phylogenetic tree of class B1 GPCRs. PCO371-sensitive and PCO371-insensitive receptors are indicated with red and blue lines, respectively. PCO371 activates members of the PTH1R clade, except PTH2R and GCGR. e, Concentration–response curves of GloSensor cAMP responses of WT and L3706.47P mutant (L370P) PTH2R following stimulation with PTH or PCO371. Symbols and error bars represent the means and s.e.m., respectively, of three independent experiments performed in duplicate.