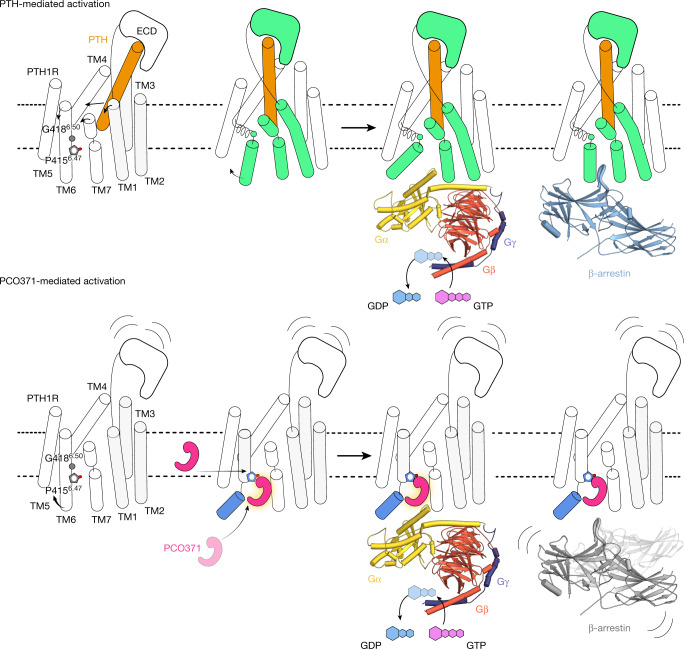
Fig. 5. Proposed mechanisms of PCO371-induced activation and signalling compared with known mechanisms of PTH-induced activation and signalling.
The distinct activation and functional selectivity mechanism of PTH1R. Top, PTH induces the rearrangement of the extracellular portions of TM1, TM6 and TM7, which causes the outwards movement of the intracellular portion of TM6 and the formation of a kink at Gly4186.50. PTH-bound PTH1R can adopt preferential conformations for G proteins and β-arrestins, respectively. Bottom, PCO371 directly moves the intracellular portion of TM6 outwards and causes the formation of a moderate kink in TM6 at Pro4156.47 without requiring extracellular rearrangement. PCO371-bound PTH1R solely adopts the preferential conformation for G proteins by stabilizing the outwards conformation of the intracellular portion of TM6. ECD, extracellular domain.