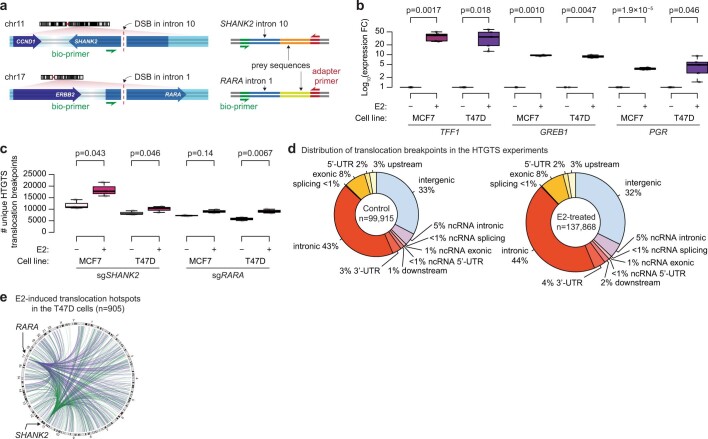
Extended Data Fig. 7. Estradiol induces transcription of its target genes and increases HTGTS translocations.
a. Design of the HTGTS experiment. Using CRISPR/Cas9 system, we induced the DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) in the intronic regions near the prominent E2-ERα binding peaks (intron 10 of SHANK2 and intron 1 of RARA). These sites are also located at the downstream neighborhood of the oncogenes of interest (ERBB2 and CCND1). We designed the library to amplify the translocated sequences to the centromeric end of the CRISPR breaks, which is in the orientation potentially forming a dicentric chromosome. b. An increased mRNA expression of canonical target genes of ERα by the E2 treatment. All three genes showed robust upregulation of their expression in both MCF7 and T47D cells. n = 5 biologically independent experiments were performed for TFF1 and PGR, and n = 3 for GREB1 in two different cell lines. Box plots in b and c indicate median (thick line), first and third quartiles (edges), and 1.5x of interquartile range (whiskers). In both, statistical comparisons were made by two-sided, two-sample t test. c. An increased number of unique HTGTS translocation breakpoints by the E2 treatment in all four experimental pairs. n = 3 biologically independent experiments were performed in each group. d. Genomic annotation of the HTGTS translocation breakpoints in the control and E2-treated experiments. e. A circos plot visualizing the hotspots E2-induced translocations (> 4-fold change by the E2 treatment) between the induced breaks and the prey regions in the T47D cells.