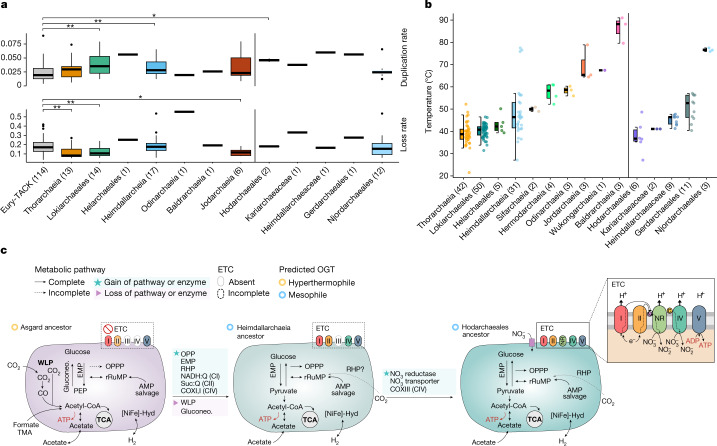
Fig. 4. Genome dynamics, OGT predictions and metabolic reconstruction of Asgard ancestors.
a, Duplication and loss rates inferred for Asgard archaeal ancestors, normalized by proteome size. P values given for each two-sided Wilcoxon-test against the median values of TACK and Euryarchaea (Eury-TACK) ancestors, where *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01 and ***P ≤ 0.001. No corrections were done for multiple comparisons. b, OGT predictions predicted by genomic features. Right, OGTs within Heimdallarchaeia. Actual values are available in Supplementary Table 5. In a and b, boxplots are represented as a central line denoting the median value, a coloured box containing the first and third quartiles of the dataset, and whiskers representing the lowest and highest values within 1.5 times the interquartile range, and sample sizes are shown within parentheses on the axis labels. c, We predict that the LAsCA transitioned from a hyperthermophilic fermentative lifestyle to a mesophilic mixotroph lifestyle. The LAsCA probably encoded gluconeogenic (Gluconeo.) pathways through the reverse EMP gluconeogenic pathway and through fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase/phosphatase (FBP A/P). The major energy-conserving step in the early Asgard ancestors could have been the ATP synthesis by fermentation of small organic molecules (acetate, formate or formaldehyde). The reverse ribulose monophosphate pathway (rRuMP) was a key pathway in the LAsCA for the generation of reducing power. The WLP appeared only present in the LAsCA. The tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle is predicted complete in all three ancestors, the Hodarchaeales common ancestor encoding the most complete ETC, and probably used nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor. Membrane-associated ATP biosynthesis coupled to the oxidation of NADH and succinate and reduction of nitrate could have been present in the LAECA. c, cupredoxin; NR, nitrate reductase; OPPP, oxidative pentose phosphate pathway; PEP, phosphoenolpyruvate; PRK: phosphoribulokinase; Q, quinone; RHP, reductive hexulose-phosphate; RuBisCO, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase; TMA, trimethylamine.