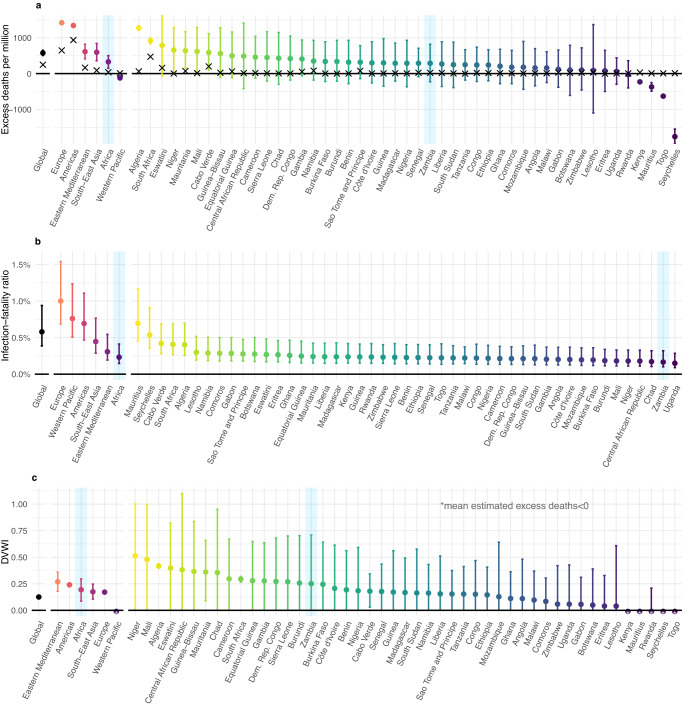
Fig. 2. Global estimates of excess mortality relative to patterns of demographic vulnerability.
Figure shows a World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates of excess mortality per million people in 2020. Points show mean and lines 95% confidence intervals from 1000 samples. Crosses show confirmed COVID-19 mortality per million people in 2020. b Estimates of region-level IFR calculated using age-specific IFR estimates from Brazeau et al.42 weighted by region population age-distribution (i.e., assuming infection equally distributed across the population). Points show median IFR and lines 95% credible intervals from 1000 draws of the joint posterior of the IFR by age curve. c Estimated demographic-vulnerability-weighted impact (DVWI), defined as the cumulative attack rate, spread uniformly by age, required to achieve a level of direct COVID-19 mortality matching the excess mortality in a assuming the posterior median IFR from b. Points and lines show median with 95% confidence intervals corresponding with 1000 draws from excess mortality estimates in a. All panels highlight in blue estimates for the WHO Africa region and Zambia for ease of identification.