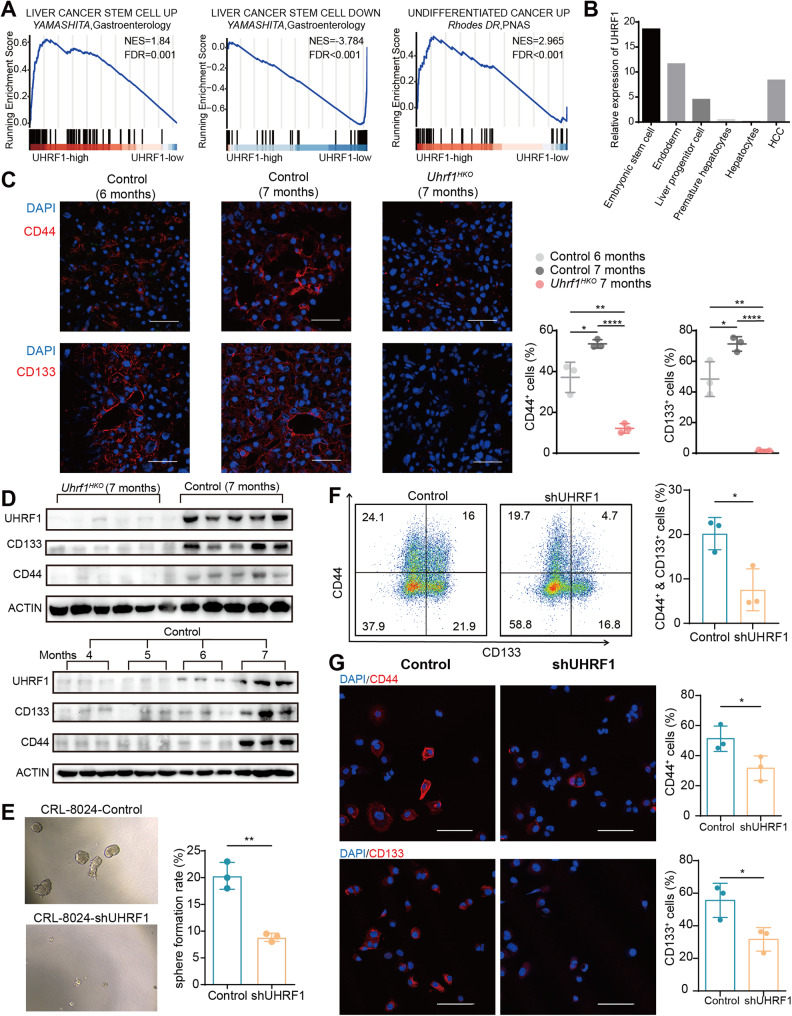
Fig. 2. UHRF1 silencing abolishes the CSC phenotype of HCC cells.
A Gene set enrichment analysis of cancer stem cell-associated gene sets in UHRF1 high versus low patients from the TCGA-LIHC dataset. B The mRNA expression of UHRF1 at different hepatic developmental stages and in HCC tumor tissues. C Immunofluorescence analysis of CD44 and CD133 expression in liver tissues at the indicated time points. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 100 μm (n = 3). D Immunoblotting analysis of the indicated proteins in liver tissues of mice at different time points. E Representative images and quantification of spheroids formed by the indicated stable cell lines (n = 3). F The CSC subpopulations were evaluated by flow cytometry. CRL-8024 cells were stained with anti-CD133-PE and anti-CD44-APC antibodies. The percentage of CD44+CD133+ cells was calculated and depicted in the bar chart (n = 3). G Immunofluorescence analysis of CD44 and CD133 expression in CRL-8024 cells. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar: 100 μm. Mean ± SD. P values were determined using unpaired Student’s t test. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001.