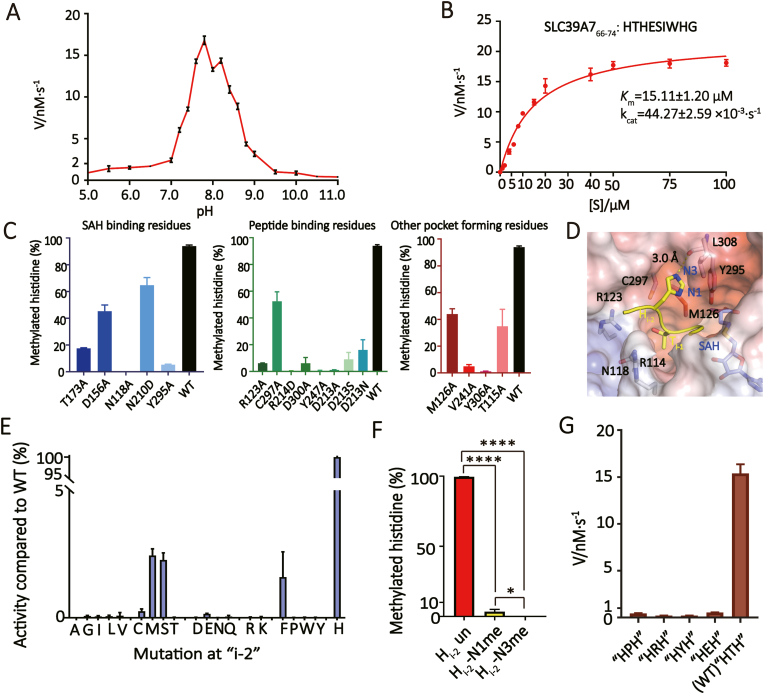
Fig. 4.
Enzymatic analyses of METTL9.(A) The methylation rate of METTL9 at different pH. The pHs were adjusted by mixing different volumes of 50 mM sodium acetate and 50 mM CAPS. The detection was carried out at intervals of 0.2 between pH 7–9 and at intervals of 0.5 for the remaining pH ranges. (B) Michaelis–Menten plots of METTL9-catalyzed histidine N1-methylation of the SLC39A766-74 peptide. The kinetic parameters, Km and kcat were listed. The reaction was carried out under 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.5, 50 mM NaCl, and 0.5 mM METTL9. (C)In vitro methylation assays of METTL9 mutants towards the SLC39A766-74 substrate. Three categories of pocket residues are shown as indicated. (D) Close-up view of histidine recognition at i-2 and i-1 position. Key METTL9 residues are shown as sticks. (E) Comparison of catalytic efficiency by METTL9 among wild type and Hi-2-altered peptide substrates. The enzymatic activities are normalized to the wild type peptide substrate. The Y-axis is expressed as the percentage activity, and the X-axis is spread as twenty proteinogenic amino acids. (F) Comparison of enzyme activities of METTL9 towards unmethylated, N1-methylated, and N3-methylated Hi-2 peptides. (G) Comparison of catalytic efficiency by METTL9 among wild type and “xi-1”-altered peptide substrates. Error bars, N = 3, One-way ANOVA with post-hoc analysis.