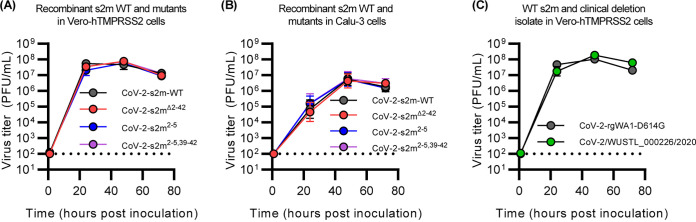
FIG 2.
The s2m is dispensable for SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. (A and B) Multistep growth curve of CoV-2-s2m-WT and mutants in Vero-hTMPRSS2 (A) and Calu-3 cells (B). Mutant strains include CoV-2-s2mΔ2–42, which contains a deletion of the s2m element; CoV-2-s2m2–5, which contains four consecutive substitutions of the stem of the s2m; and CoV-2-s2m2–5,39–42, which contains complementary substitutions predicted to restore the secondary structure of the s2m. Infectious virus titer measured in PFU per milliliter at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h postinoculation. No difference in the viral titer was detected by a two-way ANOVA with post hoc testing by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test between CoV-2-s2m-WT and all mutants for Vero-hTMPRSS2 [F(3, 20) = 1.02, P = 0.40] and for Calu-3 cells [F(3, 20) = 0.48, P = 0.7]. (C) Multistep growth curve of the infectious viral titer using a clinical isolate of SARS-CoV-2 containing a partial deletion of the s2m element (WUSTL_000226/2020) compared to a WA1 strain of SARS-CoV-2 with a D614G mutation. Viral titers were measured at 0, 24, 48, and 72 h postinoculation, and no difference in titers was detected by a two-way ANOVA with post hoc testing by Sidak’s multiple-comparison test [F(1,20) = 2.34, P = 0.16]. For all graphs, geometric means ± geometric standard deviations are depicted. The dotted line is the limit of detection of the assay.