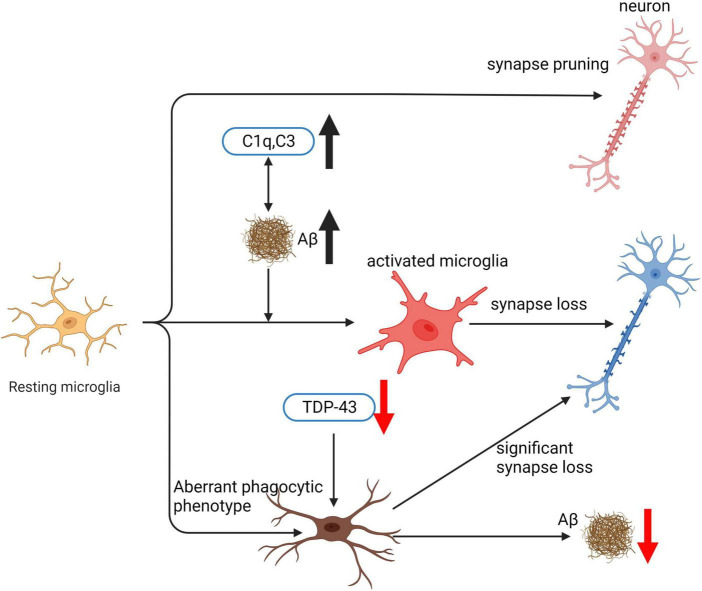
FIGURE 6.
Mechanisms of synaptic loss induced by microglia under normal and pathological conditions. This illustration depicts the various pathways through which microglia contribute to neuronal synaptic loss. Under normal circumstances, microglia participate in routine synapse pruning. However, upon aggregation of Aβ, levels of complement proteins C1q and C3 rise, which in turn promote further Aβ aggregation. This initiates a vicious cycle leading to the activation of microglia, resulting in synaptic loss in neurons. Moreover, the knockout of TDP-43 causes an aberrant phagocytic phenotype in neurons, enhancing their phagocytic function. While this increase in phagocytic activity promotes Aβ clearance, it also triggers a substantial loss of synapses in the neurons.