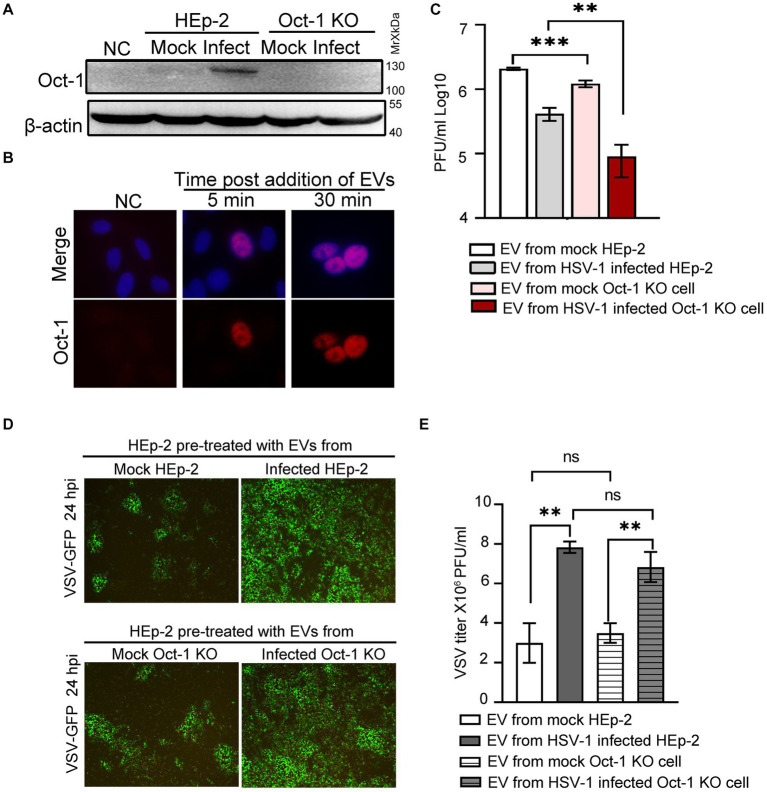
Figure 4.
Effect of EVs from HEp-2 and Oct-1 KO cells on HSV-1 or VSV-G replication in recipient HEp-2 cells. (A–E) HEp-2 and Oct-1 KO cells were mock infected or infected with HSV-1(F) at an MOI of 0.1 for 50 h, then supernatant was collected and EVs were isolated through iodixanol-sucrose gradient-based ultracentrifugation. The recipient cells were incubated with an equal volume (500 μL) of exosome-enriched fractions (fractions 1 to 6 in Figures 3D–E) for the indicated time. (A) The Oct-1 KO cells were incubated with EVs for 2 h, and then the Oct-1 protein level was examined by immunoblotting with anti-Oct-1 antibody. NC represents no exosome treatment. (B) A total of 2 × 105 Oct-1 KO cells were incubated with exosome-enriched fractions for 5 min and 30 min, and then reacted with anti-Oct-1 antibody labeled with fluorophores. (C–E) A total of 4 × 105 HEp-2 cells incubated with EVs were infected with 4,000 PFU of HSV-1 or 40,000 VSV-GFP at 37°C for 2 h. (C) At 24 hpi, cell-associated HSV-1 were titrated by a plaque assay. (D,E) At 24 hpi, green fluorescent protein (GFP) levels in HEp-2 cells treated with EVs were photographed under a fluorescence microscope (D), and VSV-GFP viruses from the supernatant were titrated by a plaque assay (E). p-values < 0.01 were marked as “**,” p-values < 0.001 were marked as “***”.