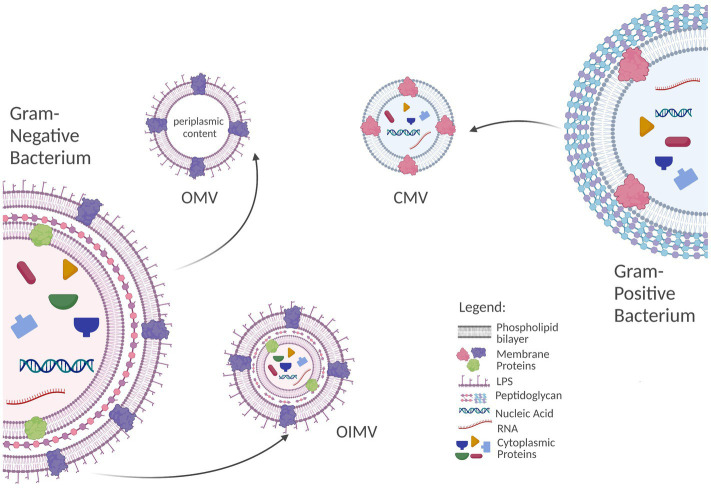
Figure 1.
Biogenesis and characteristics of bacteria-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs). Outer-inner membrane vesicles (OIMVs) are formed from Gram-negative bacteria through blebbing or in “explosive cell lysis” process. OIMVs are considered to contain all functional components of parental cells including lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and the fragments of chromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid. Outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) are the most abundant vesicle type secreted by Gram-negative bacteria. OMVs are formed through blebbing and predominantly contain periplasmic content of the parental cell. In the case of Gram-positive bacteria, the mechanism of cytoplasmic membrane vesicles (CMVs) generation is based on selective degradation of peptidoglycan cell wall layer. It might lead to the cell death which is termed “bubbling cell lysis” Created with BioRender.com.