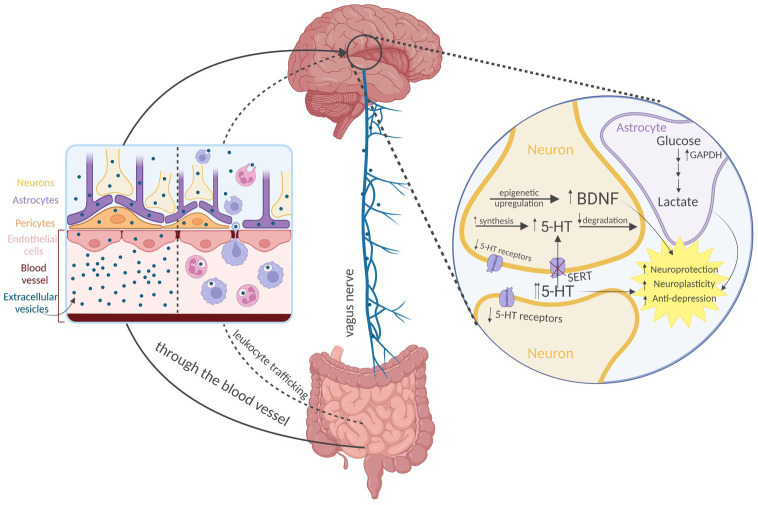
Figure 2.
Distribution and action of the psychobiotic bacteria-derived extracellular vesicles (EVs) on the brain. Direct crossing of the blood–brain barrier appears to be the predominant way of EVs transport to the brain. Other routes include vagal nerve transport and activated leukocyte trafficking. According to the current evidence, EVs from psychobiotic bacteria produce antidepressant-like effect mediated by epigenetic upregulation of neurotrophic factors (e.g., brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF), modulation of serotonergic system expression, and possibly by supplementation the astrocytes with glycolytic enzymes (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH). 5-HT—serotonin, and SERT—5HT transporter Created with BioRender.com.